Security misconfigurations have quietly become the most dangerous weakness in modern cloud environments. In 2026, attackers no longer rely on zero-day exploits, advanced malware, or nation-state tooling to breach organizations. Instead, they exploit configuration mistakes-small, often invisible errors that expose critical systems directly to the internet.
A single misconfigured cloud resource can be compromised within minutes of deployment. No vulnerability scanning. No exploit chaining. Just automated discovery followed by immediate abuse. This represents a fundamental shift in the threat landscape.
Traditional security models assumed that attacks required sophistication. Modern cloud breaches prove the opposite. Attackers now succeed by moving faster than defenders, leveraging automation, default settings, and overly permissive access controls.
This article provides a deep technical breakdown of the five most exploited security misconfigurations in 2026, explains how attackers weaponize them, and outlines practical steps to prevent cloud breaches before they happen.
What Are Security Misconfigurations?
A security misconfiguration occurs when a system, service, or application is deployed with unsafe, overly permissive, or default settings that expose it to unauthorized access.
Unlike software vulnerabilities, misconfigurations:
- Are not bugs in code
- Do not require exploitation techniques
- Are often “working as designed”
Common examples include:
- Publicly accessible cloud storage
- IAM roles with wildcard permissions
- Kubernetes service accounts bound to cluster-admin
- APIs without authentication or rate limiting
- Serverless functions with excessive privileges
Security misconfigurations are especially dangerous because they create legitimate access paths for attackers. Once discovered, attackers operate entirely within the system’s allowed behavior.
Why Misconfigurations Are the #1 Breach Vector in 2026
Several factors have made misconfigurations the dominant attack vector:
Cloud Speed vs Human Review
Cloud infrastructure evolves faster than manual security reviews can keep up with. Resources are created, modified, and destroyed continuously.
Cloud providers secure the infrastructure. Customers secure the configuration. Many organizations underestimate this responsibility.
Default-Insecure Settings
Many services prioritize usability over security, leaving dangerous defaults in place unless explicitly hardened.
Automated Attacker Tooling
Attackers use scanners that continuously enumerate:
- Cloud IP ranges
- Storage endpoints
- Open databases
- API gateways
- Kubernetes control planes
When exposure is detected, exploitation is immediate.
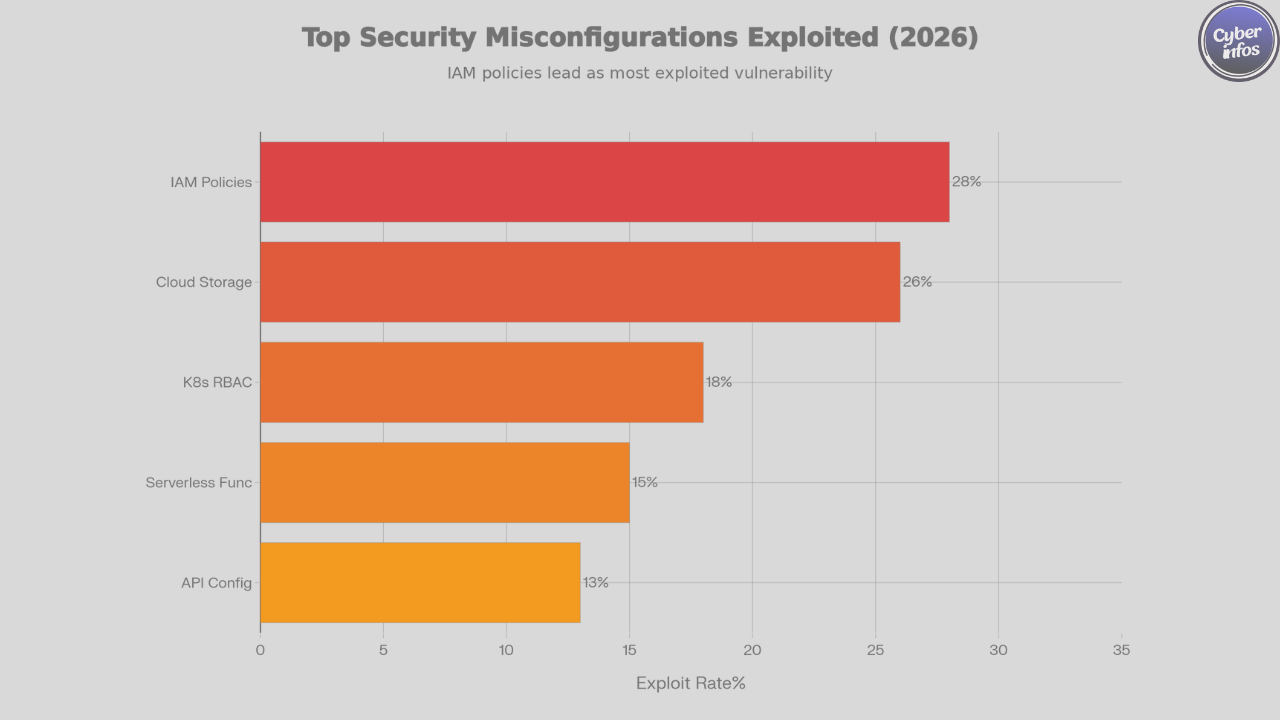
The Misconfiguration Crisis by the Numbers
The scale of cloud security misconfigurations in 2026 is staggering:
- 31% of cloud storage buckets remain publicly accessible
- Misconfiguration is the leading cause of cloud breaches
- Exposed databases receive an average of 18 attack attempts per day
- 22,900 databases were compromised in a single ransomware-driven data exposure campaign
- Hundreds of thousands of customer records exposed through misconfigured cloud environments
These incidents affect:
- Financial institutions
- Healthcare providers
- SaaS companies
- Cryptocurrency exchanges
- Government contractors
Misconfigurations are not edge cases. They are systemic failures.
Top 5 Security Misconfigurations Hackers Exploit in 2026
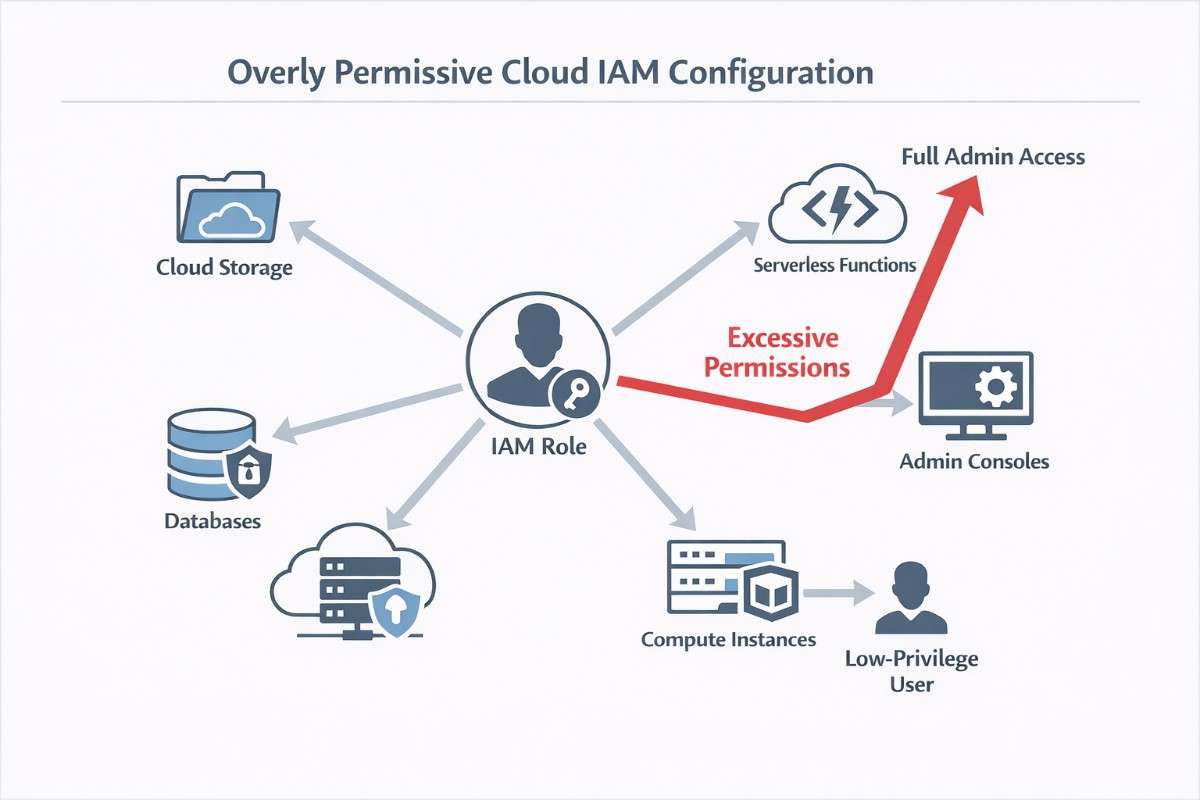
1. Overly Permissive IAM Policies and Privilege Escalation
Why IAM Misconfigurations Are So Dangerous
Identity and Access Management (IAM) controls who can do what in a cloud environment. When misconfigured, IAM becomes the fastest path to total compromise. The most common mistake: granting more permissions than necessary. Attackers do not need to exploit IAM. They simply abuse legitimate permissions.
How Hackers Exploit IAM Misconfigurations
Once a low-privileged account is compromised (via phishing, leaked credentials, or exposed keys), attackers attempt privilege escalation.
Common escalation paths include:
- Creating access keys for higher-privileged users
- Switching to older, more permissive policy versions
- Injecting inline policies into assumable roles
From there, attackers gain:
- Full administrative access
- Cross-account trust exploitation
- Persistent access through new identities
Real-World Impact
IAM misconfigurations lead to:
- Complete cloud account takeover
- Silent data exfiltration from storage and databases
- Infrastructure manipulation (EC2, Lambda, Kubernetes)
- Long-term persistence that survives password resets
Detection and Remediation
Detection
- Monitor IAM change events continuously
- Flag wildcard permissions
- Identify unused but powerful privileges
Remediation
- Enforce least privilege rigorously
- Remove policy version management from standard roles
- Require MFA for sensitive IAM operations
- Implement organization-wide guardrails
Real incident as Example
BeyondTrust Remote Support Breach (December 2024)
In late 2024, BeyondTrust uncovered suspicious activity inside its Remote Support SaaS platform. The root cause was not an exotic zero-day-it was an API key that had far more permissions than it needed.
Attackers combined this overprivileged credential with a command injection vulnerability (CVE-2024-12356, CVSS 9.8). Because the API key was static, broadly scoped, and insufficiently monitored, it became the perfect pivot. With it, attackers achieved unauthenticated remote code execution and escalated privileges across environments that should never have been reachable from a single key.
This breach illustrates a recurring IAM failure pattern: credentials outliving their purpose while retaining god-mode access.
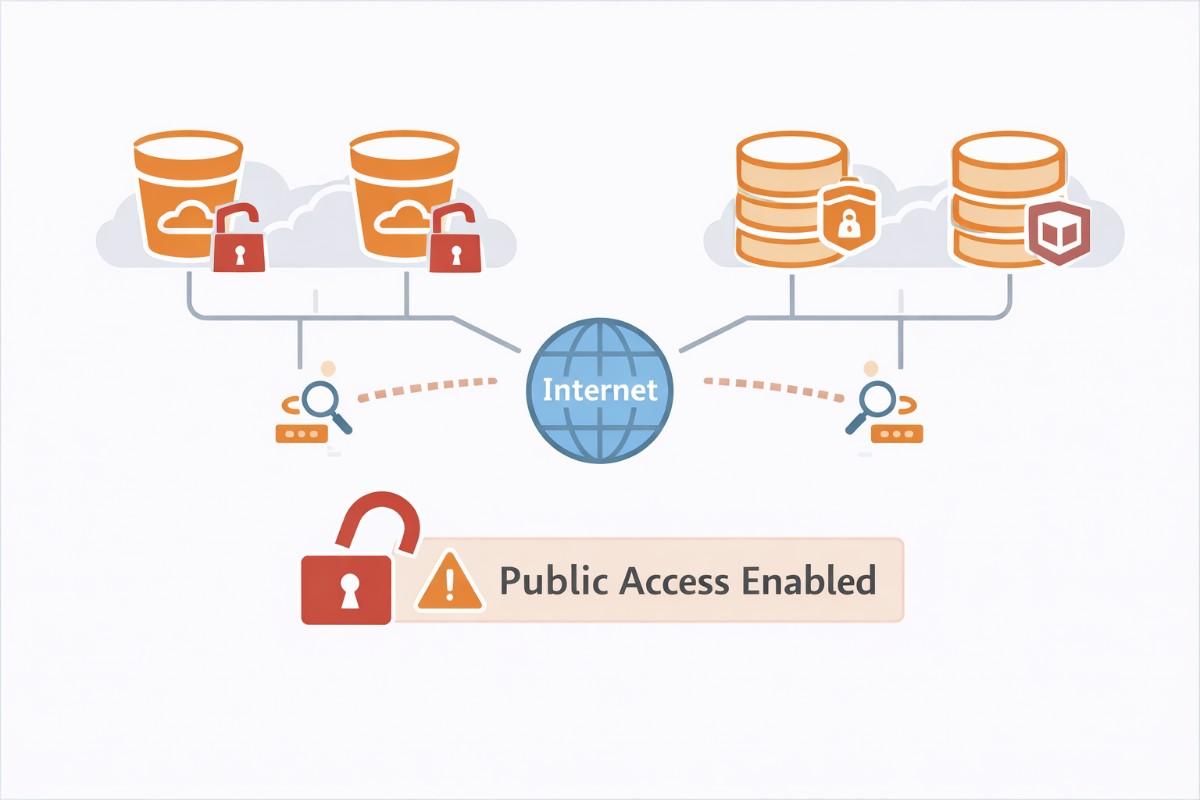
2. Publicly Exposed Cloud Storage and Databases
The Fastest Breach Path in Cloud Security
Public cloud data exposure remains the most common and fastest misconfiguration exploit.
Storage buckets and databases are often exposed due to:
- Temporary testing configurations
- Legacy access policies
- Disabled security controls
Once public, discovery is inevitable.
How Cloud Misconfiguration Attacks Happen
- Automated scanners detect exposed endpoints
- Attackers enumerate contents
- Data is downloaded or encrypted
- Breach is completed in minutes
No malware. No intrusion. Just access.
Real-World Consequences
Public cloud data exposure has led to:
- Leaked financial records
- Exposed KYC and identity documents
- Disclosure of authentication secrets
- Regulatory penalties and lawsuits
Prevention Strategy
- Enforce private-by-default storage policies
- Enable block-public-access controls globally
- Require encryption at rest and in transit
- Use temporary, signed URLs for sharing
- Continuously scan for exposure drift
Real incident as Example
Indian Bank Transfer S3 Exposure (August–September 2025)
In this case, there was no intrusion at all. Security researchers simply found an Amazon S3 bucket that allowed public read access.
Inside were more than 273,000 PDFs tied to Indian bank transfers-names, addresses, phone numbers, emails, bank account numbers, and IFSC codes. Worse, new files kept appearing, showing that this was not legacy data but an actively used production system.
Anyone with the bucket URL could download everything. No malware. No exploit chain. Just a misconfiguration quietly leaking financial data at scale.
Toyota Cloud Misconfiguration (2012–2023)
For over a decade, Toyota Motor Corporation unknowingly exposed customer data due to incorrect cloud settings. Location data, vehicle details, and personal information for roughly 2.15 million customers were accessible externally.
Toyota later acknowledged that unclear internal data-handling rules contributed to the issue—a reminder that cloud security failures are often governance failures long before they are technical ones.
Accenture S3 Bucket Exposure (2017)
In one of the most cited examples of cloud misconfiguration, Accenture left multiple S3 buckets publicly accessible. The exposed data included API keys, VPN credentials, certificates, plaintext and hashed passwords, and internal database dumps totaling over 130 GB.
The buckets were secured quickly once reported-but until then, the keys to client environments were effectively sitting on the open internet.
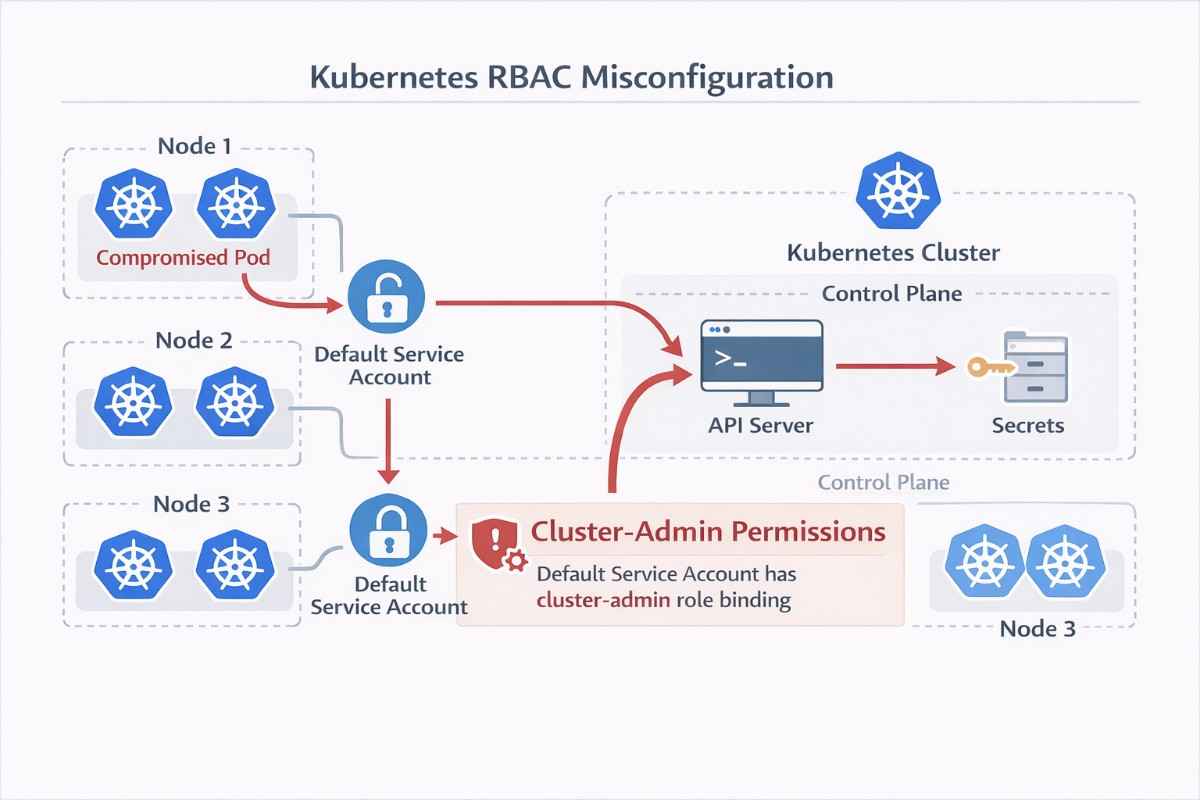
3. Kubernetes RBAC Misconfiguration
Why Kubernetes Misconfigurations Are Explosive
Kubernetes controls some of the most critical workloads in modern infrastructure. RBAC misconfigurations allow attackers to move from one pod to full cluster control. The most dangerous mistake: Binding cluster-admin to default service accounts.
Typical Attack Path
- Attacker compromises a container
- Service account token is harvested
- Kubernetes API is accessed
- Malicious workloads are deployed
- Secrets and data are exfiltrated
This is not theoretical-it is one of the most common real-world Kubernetes breaches.
Impact of a Compromised Cluster
- Full workload compromise
- Secret theft
- Supply-chain attacks
- Persistent backdoors
Hardening Kubernetes RBAC in 2026
- Disable automatic token mounting
- Scope permissions to namespaces
- Never bind cluster-admin broadly
- Audit RBAC continuously
- Enforce Pod Security Standards
Real incident as Example
Exposed Kubernetes API Server (2025)
During routine internet scanning, an attacker found a Kubernetes API server exposed to the public. Authentication relied solely on TLS certificates, and the default service account had been granted cluster-admin privileges.
That single mistake collapsed the entire security boundary. By compromising just one pod, the attacker gained full control over the cluster-workloads, secrets, and nodes included.
This scenario plays out repeatedly in real environments: default accounts treated as harmless, then quietly elevated until they become catastrophic.
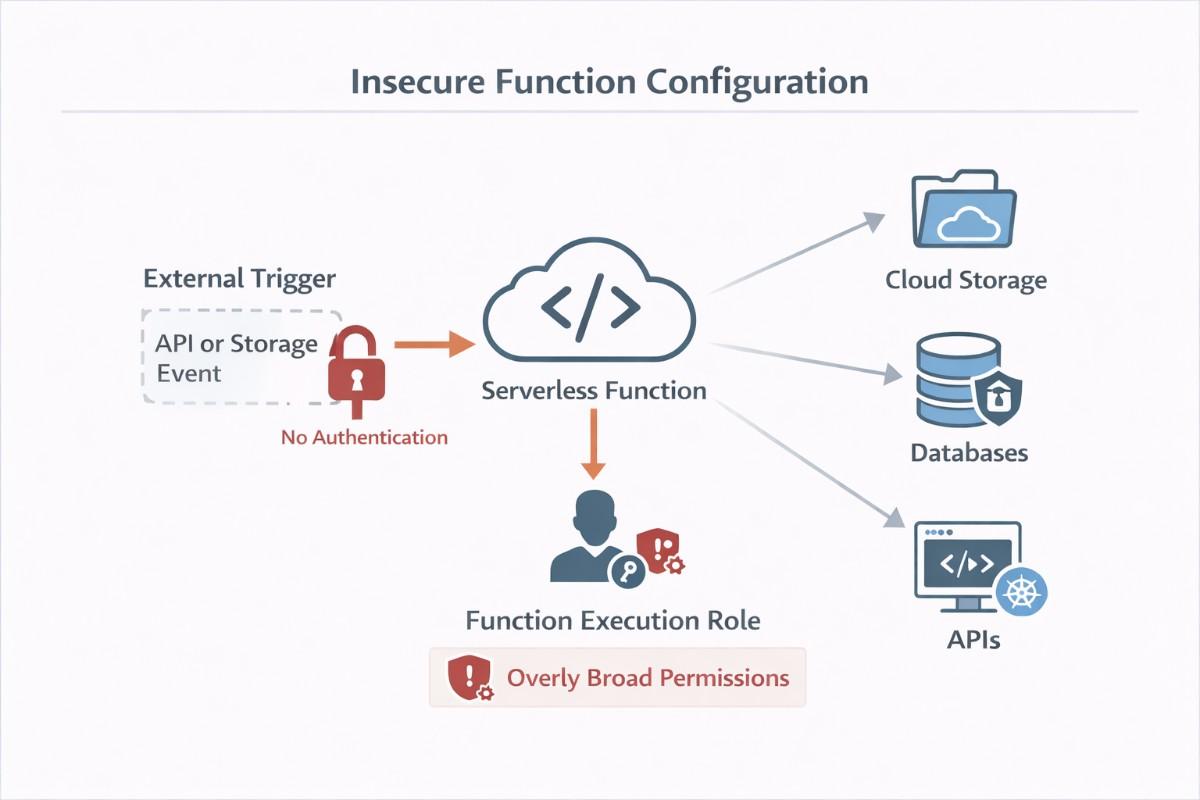
4. Insecure Serverless Function Configurations
Why Serverless Security Risks Are Growing
Serverless functions run with powerful permissions but often lack traditional security controls.
Common mistakes include:
- Over-privileged execution roles
- Public API triggers without authentication
- Unsafe event handling
How Attackers Abuse Serverless Misconfigurations
When a function is compromised:
- Temporary cloud credentials are exposed
- Attackers access internal services
- Persistence is established through new resources
Because functions scale automatically, attacks can spread rapidly.
Prevention Measures
- Apply least privilege per function
- Enforce authentication on all triggers
- Validate all event input
- Separate execution roles
- Monitor function behavior continuously
Real incident as Example
AWS Lambda Pickle Deserialization Attempt (2024)
A Python-based Lambda function accepted serialized input using Pickle-an unsafe design choice. An attacker attempted to abuse this to extract environment variables, including credentials, and exfiltrate them to an external server.
Detection tooling stopped the attack before data left the environment, but the risk was clear: once those credentials were stolen, the attacker could access everything the function was authorized to touch.
AWS Lambda S3 Trigger Backdoor (2023)
In another case, attackers exploited an unsecured S3 trigger connected to a Lambda function. By uploading a specially crafted file, they caused the function to execute malicious code.
Because the function ran with legitimate permissions, the compromise blended in with normal activity and went unnoticed until the attackers were deeply embedded.
Serverless failures often look harmless at first—until you realize functions inherit trust far beyond their code size.
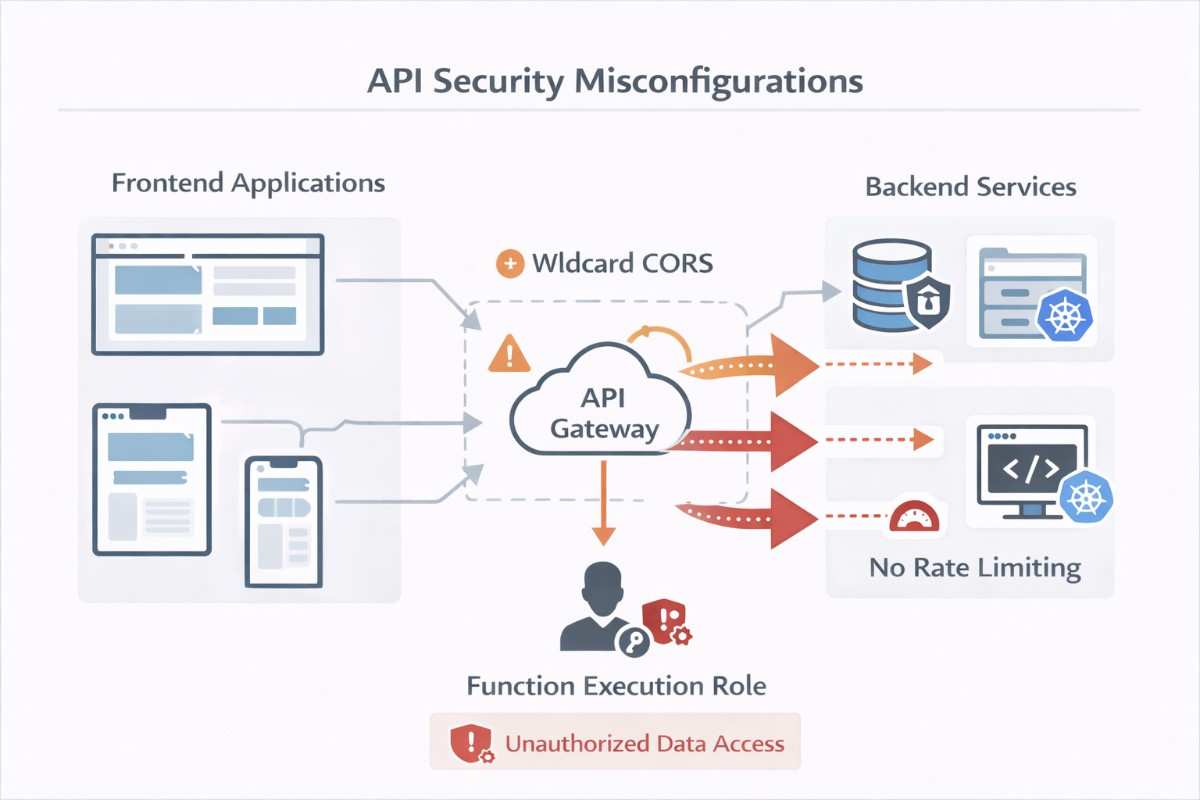
5. API Security Misconfigurations
APIs: The Soft Underbelly of Cloud Apps
APIs connect everything—and misconfigurations expose everything.
Common API security misconfigurations:
- Overly permissive CORS policies
- Missing HTTPS enforcement
- Weak or missing authentication
- No rate limiting
- Verbose error messages
Exploitation Outcomes
API misconfigurations lead to:
- Account enumeration
- Data scraping
- Credential theft
- Remote code execution
API Hardening Essentials
- Enforce TLS everywhere
- Restrict CORS origins strictly
- Implement OAuth or properly validated JWTs
- Rate-limit aggressively
- Log and monitor all requests
Real incident as Example
FinTech CORS Misconfiguration Breaches (January 2025)
Security researcher Alex Birsan documented widespread abuse of APIs that used wildcard CORS policies (Access-Control-Allow-Origin: *) while also allowing credentials.
This combination allowed attackers to silently make authenticated API calls from victims’ browsers. Across 35 financial services APIs, more than 2 million users were affected. At one FinTech company alone, 1.2 million accounts were compromised.
The APIs worked exactly as configured-which was the problem.
Capital One AWS WAF Misconfiguration (2019)
The breach at Capital One began with a misconfigured AWS web application firewall. That configuration allowed SSRF requests to reach internal services, exposing cloud credentials.
Those credentials were then used to extract over 100 million credit card application records. The access occurred in March 2019—but the company did not learn about it until months later.
The failure was not encryption, nor cloud infrastructure—it was trust misplaced in a security control assumed to be “set and forget.”
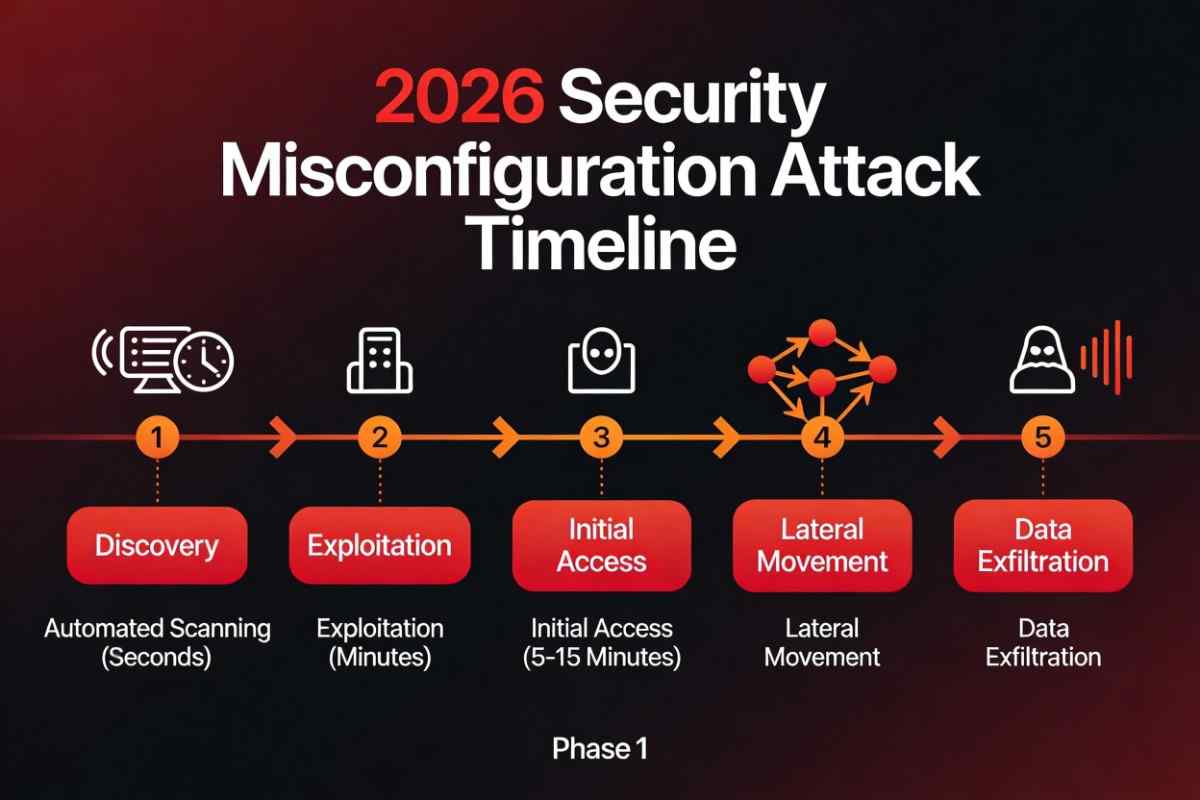
The Minutes-to-Breach Attack Timeline
One of the most dangerous realities of cloud misconfigurations is speed.
Once exposed:
- Discovery occurs within minutes
- Exploitation follows immediately
- Data loss often precedes detection
This compressed timeline makes reactive security ineffective. Prevention must occur before exposure.
Detection and Prevention Strategies
Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM)
CSPM tools provide:
- Continuous configuration monitoring
- Attack path analysis
- Automated remediation
- Compliance mapping
They are essential for managing scale and speed.
Infrastructure-as-Code (IaC) Scanning
Shift-left security ensures:
- Misconfigurations are blocked before deployment
- Security policies are enforced automatically
- Drift is detected immediately
Best Practices to Prevent Security Misconfigurations in 2026
- Automate configuration enforcement
- Assume breach scenarios
- Apply least privilege universally
- Monitor continuously
- Test exploitability, not just compliance
- Train developers on cloud security fundamentals
Final Thoughts
Security misconfigurations dominate breaches because cloud infrastructure moves faster than outdated security processes.
Organizations that succeed in 2026:
- Automate detection and remediation
- Embed guardrails into pipelines
- Treat configuration as a continuous discipline
Misconfigurations are not inevitable.
They are preventable-with discipline, automation, and intent.
FAQs
Why are misconfigurations the top breach vector?
Because they require no exploitation and are easily discovered.
How can organizations stop cloud breaches in 2026?
Through automation, least privilege, CSPM, and IaC scanning.
What are security misconfigurations?
Security misconfigurations are incorrect or unsafe system settings that expose applications, cloud resources, or data to attack.
Why are misconfigurations the top breach vector in 2026?
Because they are easy to exploit, widely present, and often exposed directly to the internet.
How do hackers exploit cloud misconfigurations in 2026?
Through automated scanning, enumeration, and abuse of legitimate cloud features.
How can organizations stop cloud breaches in 2026?
By combining CSPM, IaC scanning, least privilege, and continuous monitoring.
Disclaimer
This article is published for informational and educational purposes only. It is intended to provide technical insight into common cloud security misconfigurations and observed attack patterns, not to serve as legal, compliance, or security advice.
The examples, breach incidents, and statistics referenced are based on publicly reported information, security research, and industry analysis available at the time of writing. While every effort has been made to ensure accuracy, cloud platforms, threat techniques, and security controls evolve rapidly, and conditions may change without notice.
Readers should not rely solely on this content to secure production environments. Security decisions should be made based on organization-specific risk assessments, internal policies, and guidance from qualified security professionals.
Any mention of third-party companies, products, or incidents is for educational context only and does not imply endorsement, attribution of fault beyond publicly disclosed findings, or current security posture.
The authors and publisher of cyberinfos.in disclaim any liability for actions taken or not taken based on the information provided in this article.