This cybersecurity weekly report for 11–17 January 2026 documents a week defined by scale, speed, and systemic exposure. Across industries, attackers demonstrated that exploiting trust relationships—APIs, third-party vendors, and automation platforms—remains more effective than breaching hardened perimeters. High-impact data exposures in social media, healthcare, and e-commerce created immediate downstream risks, particularly phishing, identity fraud, and account takeover attempts.
At the same time, defendersansomware operators accelerated activity despite declining ransom payments, signaling a shift toward volume-driven campaigns, double- and triple-extortion models, and monetization through data resale rather than encryption alone. The disclosure of a critical unauthenticated remote code execution vulnerability in the n8n workflow automation platform intensified defender workload, especially for organizations that had rapidly adopted automation without equivalent security governance.
Patch management again proved decisive. Microsoft’s January Patch Tuesday addressed over one hundred vulnerabilities, including an actively exploited zero-day, reinforcing the operational reality that patch latency is now one of the most exploitable weaknesses in enterprise environments. Threat intelligence reporting also highlighted a notable evolution in initial-access tactics: attackers increasingly leveraged messaging platforms, developer tools, and trusted system utilities to bypass email-centric defenses.
Regulatory pressure rose in parallel. New privacy and cybersecurity enforcement frameworks in the UK, EU, and multiple US states entered force or moved closer to implementation, raising compliance expectations for transparency, data minimization, and incident response readiness. Collectively, this week underscored a mature threat environment where impact is driven less by novelty and more by the rapid exploitation of known weaknesses at global scale.
Major Incidents
Instagram User Data Exposure and Secondary Abuse
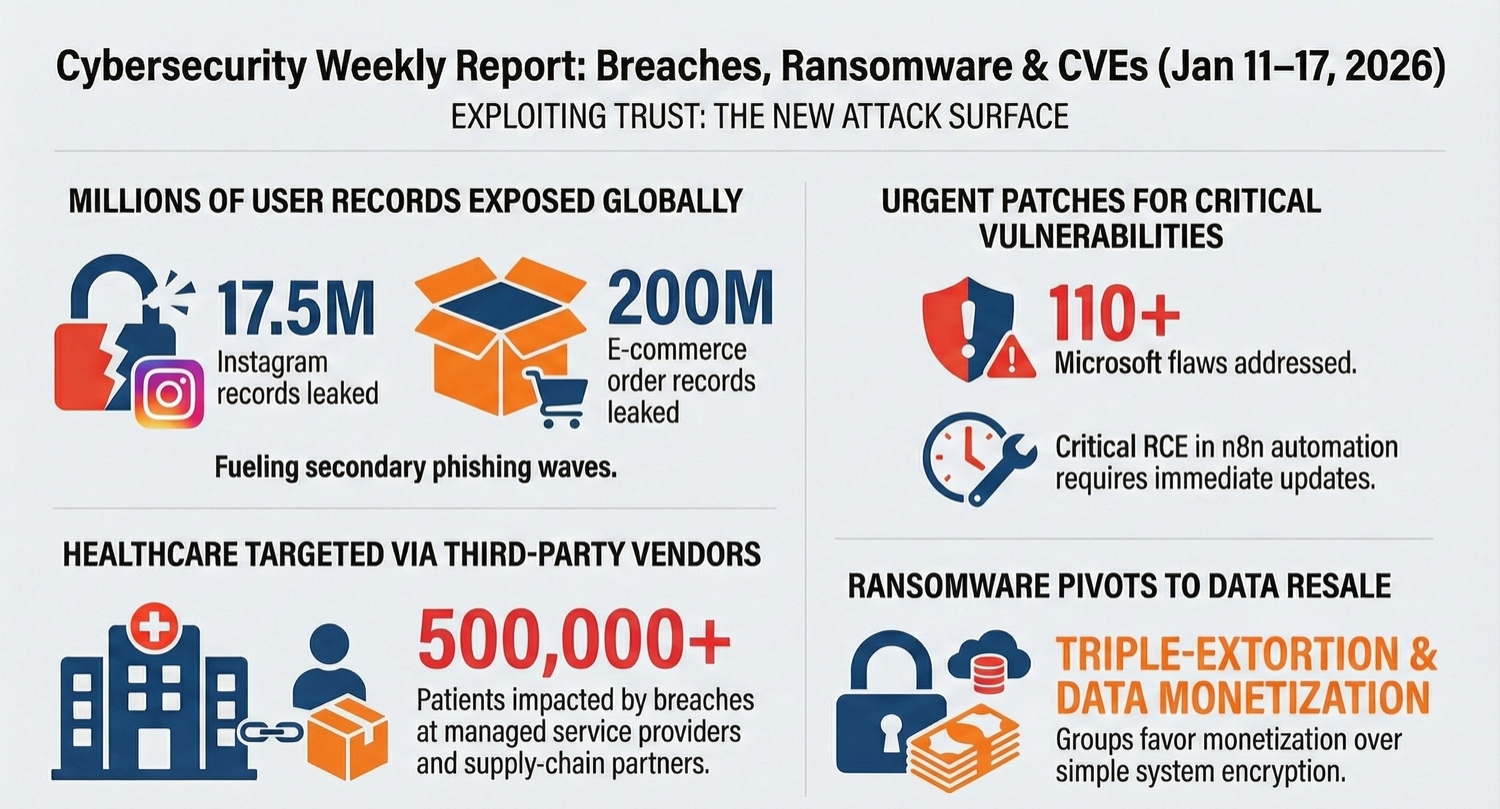
During the week, a dataset containing approximately 17.5 million Instagram user records circulated on underground forums, quickly becoming fuel for large-scale phishing campaigns. The exposed data included names, email addresses, phone numbers, and partial location details—sufficient to craft convincing social-engineering lures. Parent company Meta stated that no current systems were breached and attributed the data to historical scraping activity rather than a fresh intrusion.
Despite this clarification, the practical impact was immediate. Security firms observed waves of fraudulent password-reset emails and account-verification messages targeting affected users within 24 hours of the data’s release. The incident reinforced a recurring lesson in this cybersecurity weekly report: even “old” data exposures remain operationally dangerous when attackers combine them with timely social-engineering campaigns and automation.
Healthcare Breaches via Third-Party Compromise
Healthcare organizations were again disproportionately affected, primarily through vendor relationships. Allegheny Health Network disclosed that unauthorized access at a managed service provider exposed sensitive information for nearly 300,000 patients. The compromised data included names, dates of birth, Social Security numbers, insurance information, and detailed treatment records.
Separately, Asheville Eye Associates confirmed a ransomware-linked intrusion affecting roughly 200,000 patients. Attackers claimed exfiltration of hundreds of gigabytes of protected health information prior to encryption. While financial data was reportedly not exposed, the breadth of medical and identity information created long-term risk for affected individuals.
These incidents illustrated a persistent systemic weakness: healthcare entities often rely on third-party providers with extensive network access, yet lack continuous visibility into those vendors’ security posture. In both cases, attackers remained undetected for weeks, highlighting monitoring and governance gaps rather than advanced exploitation.
E-Commerce Supply-Chain Breach Impacting Cryptocurrency Customers
A breach at Global-e, an international e-commerce platform, cascaded across multiple merchants, including hardware wallet manufacturer Ledger. More than 200 million order records were reportedly exposed, containing customer names, addresses, email addresses, phone numbers, and purchase metadata. Although no payment card data or cryptographic secrets were compromised, the exposure created fertile ground for targeted scams against cryptocurrency users.
The incident exemplified modern supply-chain risk: organizations inherit the security failures of platforms that handle customer data on their behalf. Attackers increasingly favor these centralized service providers, where a single compromise yields data from dozens or hundreds of downstream brands.
Media Subscriber Data Exposure
Subscriber data associated with a major technology publication was exposed through insecure access controls in an account management system. The issue stemmed from predictable identifiers and insufficient authorization checks, allowing unauthorized access to subscriber records. While the incident did not involve malware or ransomware, it demonstrated how basic application security failures can still lead to large-scale data exposure.
Across these major incidents, a consistent pattern emerged: most damage resulted not from zero-day exploitation, but from long-standing weaknesses in APIs, access control, and third-party governance.
New Vulnerabilities & Patches
Critical n8n Remote Code Execution Vulnerability
One of the most significant developments in this cybersecurity weekly report was the disclosure of a critical unauthenticated remote code execution vulnerability in n8n, a popular workflow automation platform. The flaw allowed attackers to manipulate request parsing logic, leading to arbitrary file access, credential extraction, administrative session forgery, and ultimately full remote code execution.
The vulnerability affected a wide range of deployed versions and was particularly dangerous for internet-facing instances. Public proof-of-concept code emerged rapidly, and automated scanning activity was observed shortly thereafter. Security teams were advised to upgrade immediately, as no reliable mitigations existed short of patching or taking affected services offline.
This incident highlighted the growing risk associated with low-code and automation platforms. While these tools deliver operational efficiency, they also concentrate privileges and credentials, making them attractive targets when security design lags behind adoption.
Microsoft January Patch Tuesday
Microsoft’s January 2026 Patch Tuesday addressed more than 110 vulnerabilities across Windows, Office, and server products. The release included multiple critical flaws and at least one zero-day vulnerability confirmed as actively exploited in the wild. A significant proportion of the issues involved elevation of privilege and remote code execution, reinforcing the importance of timely patch deployment across endpoints and servers.
Particular attention was drawn to vulnerabilities in core Windows components and file-system handling, which could enable attackers with limited access to escalate privileges or execute arbitrary code. Organizations running mixed on-premises and cloud-hosted Windows environments faced added complexity in testing and deployment, yet the active exploitation status made deferral a high-risk decision.
Exploitation Trends
Across disclosed vulnerabilities, a clear trend persisted: attackers prioritized flaws that were easy to weaponize and widely deployed rather than technically exotic. Public proof-of-concept availability continued to be a reliable predictor of exploitation, compressing the window between disclosure and active abuse to days—or hours in some cases.
For defenders, the week reinforced the need for asset visibility. Many organizations struggled to determine whether vulnerable components, particularly automation platforms and embedded services, were present in their environments at all.
Ransomware Activity
Group Activity and Market Dynamics
Ransomware activity remained high throughout the week, despite evidence that overall ransom payments declined compared to previous years. Groups such as Qilin maintained dominant positions by sustaining attack volume, while others experimented with rebranding, affiliate recruitment, and diversified extortion tactics.
Rather than relying solely on encryption, many groups emphasized data theft, public shaming, and regulatory pressure as leverage. This approach reduced dependence on victims’ willingness to restore systems quickly and increased the likelihood of at least partial monetization through data resale.
Notable Attacks
Several mid-sized organizations across construction, professional services, and manufacturing reported ransomware incidents during the week. While few represented household names, the cumulative impact was significant: operational disruption, regulatory notification costs, and long-term reputational damage.
Healthcare once again featured prominently, reflecting both the sector’s data value and its limited tolerance for downtime. Attackers appeared willing to negotiate but maintained aggressive timelines, reflecting competitive pressure within the ransomware ecosystem.
Payment and Negotiation Trends
Negotiation data indicated continued downward pressure on ransom amounts, with more victims refusing to pay or successfully negotiating reductions. In response, attackers increasingly threatened secondary consequences, such as notifying regulators or contacting customers directly.
This shift suggested a maturing ransomware market in which psychological and regulatory leverage now plays a central role, rather than technical lockout alone.
Threat Intelligence
Nation-State Campaigns
Threat intelligence reporting during the week highlighted sustained activity from multiple nation-state actors. Russia-aligned groups intensified spear-phishing operations using messaging platforms rather than email, exploiting gaps in monitoring and user awareness. China-linked actors focused on critical infrastructure and government-adjacent targets, combining credential theft with hands-on-keyboard techniques to maintain persistence.
Iran-aligned campaigns targeted diplomatic, financial, and telecommunications sectors, often using custom malware and social-engineering lures tailored to regional contexts. These operations emphasized espionage and long-term access rather than immediate disruption.
Emerging Tactics, Techniques, and Procedures
A notable trend was the abuse of trusted system utilities and developer tools to execute malicious payloads. By leveraging legitimate binaries, attackers reduced the likelihood of detection by traditional signature-based defenses.
Another key development was the continued rise of ClickFix-style social-engineering campaigns, in which users were tricked into executing commands under the guise of resolving fake system errors. These techniques blurred the line between technical exploitation and user manipulation, complicating prevention efforts.
Indicators of Compromise
Threat researchers released updated indicators associated with phishing domains, malicious infrastructure, and command-and-control servers used in active campaigns. Organizations were urged to integrate these indicators into detection systems and to monitor for anomalous use of legitimate administrative tools.
Industry News
Regulatory Developments
The regulatory environment continued to tighten. In the UK, updates to data-protection law took effect, introducing new enforcement powers and clarifying lawful bases for data processing, including certain AI-related activities. Across the European Union, new procedural rules aimed to harmonize GDPR enforcement entered force, promising faster and more consistent cross-border investigations.
In the United States, multiple state-level privacy laws became effective, expanding consumer rights and imposing new obligations on businesses regarding data security, transparency, and risk assessment. Together, these changes increased the cost of non-compliance and elevated cybersecurity from a technical concern to a board-level governance issue.
Corporate and Research Announcements
Security vendors released new research examining the intersection of artificial intelligence and cybersecurity, predicting both increased attacker automation and improved defensive analytics. Industry groups emphasized the need for AI governance frameworks to accompany adoption, warning that unmanaged AI systems could introduce new classes of risk.
Tool Updates
Several security tools and frameworks received notable updates during the week. n8n released patched versions addressing its critical vulnerability, urging immediate upgrades. Microsoft updated Defender capabilities in conjunction with its monthly security releases, improving detection for privilege-escalation attempts and suspicious use of system utilities.
Open-source and standards bodies continued to promote AI risk-management frameworks, reflecting growing consensus that governance must evolve alongside technical controls.
Looking Ahead
The coming week is likely to see continued exploitation of recently disclosed vulnerabilities, particularly in automation and workflow platforms. Security teams should expect sustained phishing activity leveraging newly exposed datasets and ongoing ransomware pressure against healthcare and professional services.
Defenders should prioritize asset discovery, patch deployment, and third-party risk assessments, while leadership teams prepare for increased regulatory scrutiny. As this cybersecurity weekly report demonstrates, resilience in 2026 depends less on preventing every intrusion and more on reducing dwell time, limiting blast radius, and responding decisively when incidents occur.
Final Thoughts
This cybersecurity weekly report highlights how quickly today’s threat landscape is evolving and why constant vigilance is no longer optional. The week of 11–17 January 2026 showed that attackers are successfully exploiting trust through third-party vendors, automation platforms, and social engineering rather than relying on complex technical attacks.
Large-scale data exposures, persistent ransomware pressure, and rapidly exploited vulnerabilities continue to test the resilience of organizations across all sectors. By tracking these developments through a clear and timely cybersecurity weekly report, security teams and decision-makers can better prioritize patching, strengthen risk management, and improve preparedness for the threats that lie ahead.

