In 2025, the digital landscape is more volatile than ever. With global data breach costs averaging $4.44 million and ransomware attacks shifting toward “double extortion,” businesses can’t rely on firewalls alone. The question is no longer if you’ll face a cyber incident, but how financially prepared you’ll be when it happens. That’s exactly why cyber liability insurance has become one of the most essential layers of protection for any organization.
This guide breaks down the most serious cyber risks today—from AI-driven social engineering to supply chain failures—and explains how a strong cyber insurance policy helps protect your bottom line when things go wrong.

Ransomware 2.0: Data Theft & Double Extortion
Ransomware remains the most financially devastating threat facing businesses. But attackers have upgraded their playbook. Instead of simply locking systems, they now steal sensitive data and threaten to leak it publicly if a ransom isn’t paid—an aggressive strategy known as “double extortion.”
The Risk Profile
- Targeting: Attackers have moved from broad, indiscriminate attacks to highly targeted strikes on industries like healthcare, finance, and legal.
- Impact: Severe business interruption and long-term reputational harm.
- Statistic: In 2024, nearly 40% of large cyber claims involved data theft, significantly increasing settlement costs.
How Insurance Covers It
A comprehensive cyber liability insurance quote typically includes several protections specifically designed for ransomware incidents.
- Extortion Payments: Policies may cover ransom demands, but only with explicit insurer approval.
- Forensic Investigation Costs: Covers specialized cybersecurity experts who assess the breach, contain the damage, and negotiate with attackers.
- Data Restoration: Pays for recovering data from backups or rebuilding systems corrupted by the attack.
Note: Many insurers now require evidence of immutable backups and Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) before offering ransomware coverage.
Social Engineering & AI-Driven Fraud
The “human element” continues to drive most breaches, playing a role in over 68% of them. With the explosion of Generative AI, cybercriminals now deploy deepfakes to impersonate executives or vendors, convincing employees to send large transfers or approve fraudulent requests.
The Risk Profile
- Business Email Compromise (BEC): Attackers break into legitimate email accounts and initiate unauthorized transfers.
- Deepfakes: Realistic voice and video simulations designed to bypass security procedures.
- Phishing: Targeted spear-phishing attacks that evade traditional spam filters.
How Insurance Covers It
Standard general liability insurance won’t cover social engineering losses. You need a cyber crime insurance rider or a standalone cyber policy.
- Funds Transfer Fraud Coverage: Reimburses direct losses from fraudulent wire transfers.
- Social Engineering Fraud Endorsement: Covers losses when employees are manipulated into willingly transferring funds.
- Invoice Manipulation Coverage: Protects against altered vendor payment instructions following a breach.
Supply Chain & Third-Party Risks
Your business is only as resilient as the vendors you rely on. If a cloud provider, payment processor, or software partner is compromised, your operations can still be disrupted—even if your own environment isn’t breached.
The Risk Profile
- Dependency: Heavy reliance on third-party SaaS platforms for everyday operations.
- Cascading Failures: A single vendor breach can impact hundreds of downstream businesses, as seen in the SolarWinds and Kaseya attacks.
How Insurance Covers It
This is where business interruption coverage becomes indispensable.
- Contingent Business Interruption (CBI): Replaces lost income when a crucial third-party vendor goes offline due to a cyber event.
- Third-Party Liability: Covers legal defense and settlements if clients sue you because a vendor’s breach exposed their data.
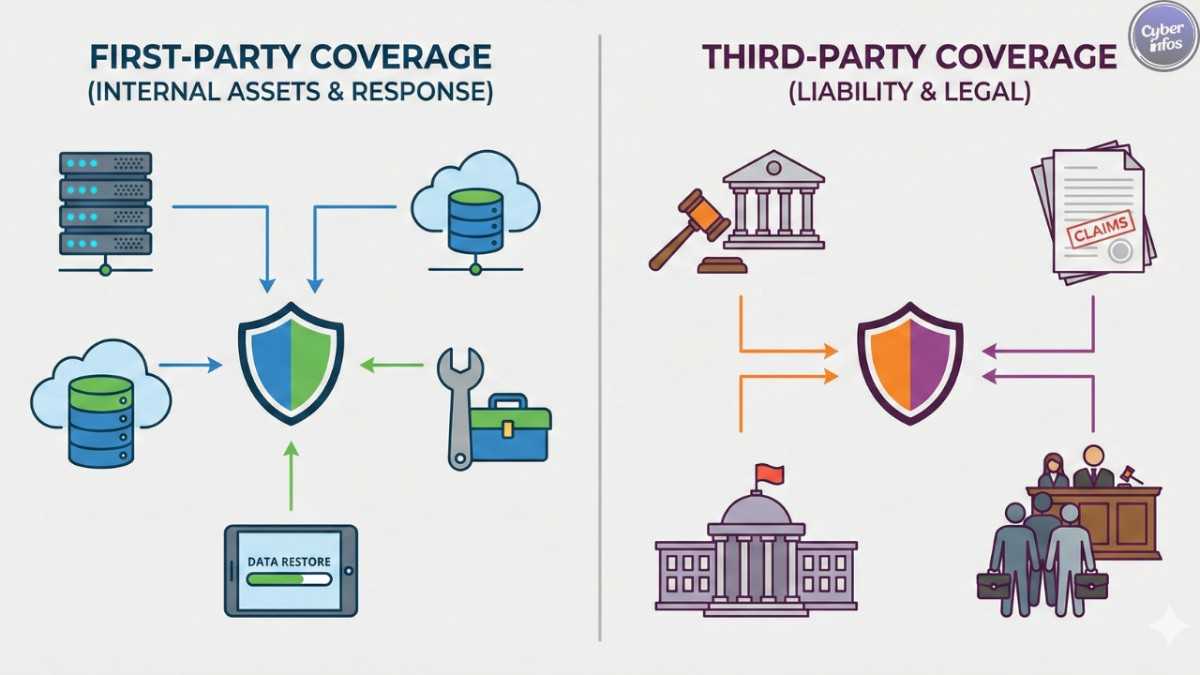
Comparison: First-Party vs. Third-Party Coverage
Understanding the distinction between these two coverage types is essential when assessing cyber insurance cost.
| Feature | First-Party Coverage | Third-Party Coverage |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Your own business assets and costs. | Liability to others (clients, regulators). |
| Key Inclusions | Data recovery, business interruption, ransom payments. | Legal defense fees, regulatory fines, settlement costs. |
| Best For | Getting your business back online quickly. | Protecting against lawsuits and class actions. |
| Example Scenario | Your server is encrypted; you lose 3 days of revenue. | You leak 5,000 customer credit card numbers; they sue you. |
Regulatory Fines and Legal Defense
With regulations like GDPR, CCPA, and new SEC disclosure requirements, the legal consequences of a breach often surpass the technical damage.
The Risk Profile
- Class Action Lawsuits: Customers file claims for negligence after their PII (Personally Identifiable Information) is stolen.
- Regulatory Penalties: Fines for failing to notify affected individuals within required timelines.
How Insurance Covers It
Cyber liability insurance helps protect your financial stability when legal issues arise.
- Privacy Liability: Covers defense costs and settlements tied to privacy-related lawsuits.
- Regulatory Fines & Penalties: Reimburses fines from regulatory agencies (where legally allowed).
- Notification Costs: Pays for required breach notifications and post-incident credit monitoring services.
EU GDPR Official Portal: For regulatory rules, penalties, and compliance updates.
FAQ: Cyber Insurance Essentials
Q1: How much does cyber insurance cost for a small business?
The average cyber insurance cost varies, but small businesses generally pay between $500 and $5,000 annually depending on revenue, industry, and their security maturity.
Q2: Does general liability insurance cover cyber attacks?
No. General liability covers bodily injury and property damage. It usually excludes data breach insurance claims and losses from cybercrime.
Q3: What triggers a business interruption claim?
A claim is triggered when a cyber event—such as a breach or malware—causes a partial or full shutdown of operations and results in income loss.
Q4: Will insurance cover a ransom payment?
Most policies offer this coverage, but approval isn’t automatic. Insurers typically require consent before a ransom is paid.
Q5: What is “social engineering fraud” coverage?
It covers financial losses when employees are deceived into transferring funds, often through phishing. These limits are usually lower than the main policy.
Q6: What are the main exclusions in cyber policies?
Common exclusions include acts of war, failure to maintain minimum security standards (such as outdated systems), and intellectual property theft.
Final thoughts
The cyber threat landscape of 2025 demands a layered defense strategy. Firewalls and MFA help prevent attacks, but cyber liability insurance is what cushions the financial fallout when prevention fails. From covering forensic investigation costs to reimbursing lost revenue during outages, the right policy ensures a cyber incident doesn’t escalate into a business-ending disaster. As you refine your risk management plan this year, make sure you secure a policy robust enough to address the cyber risks today and the challenges ahead.
Primary Keyword: Cyber risks today
Used Keywords: Cyber liability insurance, ransomware, social engineering, business interruption coverage, data breach insurance cost, cyber insurance cost, forensic investigation costs, contingent business interruption, cyber crime insurance.