The recent PayPal data breach didn’t begin with ransomware headlines or a dramatic network intrusion. Instead, it unfolded quietly inside a specialized financial workflow used by small businesses.
What Happened in the PayPal Working Capital Breach?
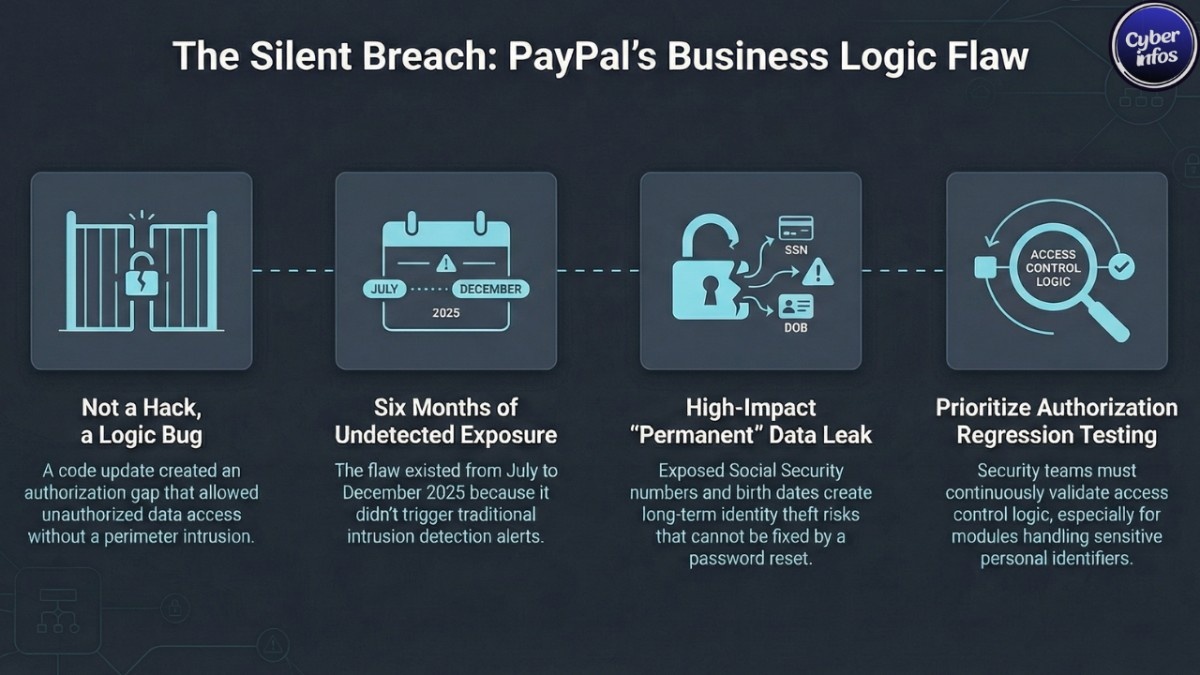
PayPal confirmed that a code update introduced a bug into its PayPal Working Capital (PPWC) loan application. The flaw created an authorization gap essentially a business logic vulnerability that allowed unauthorized individuals to access certain customer data through the interface.
The exposure reportedly lasted from July 1 to December 13, 2025. The issue was discovered on December 12 and rolled back the following day.
Importantly, PayPal characterized this as a software error rather than a traditional external system compromise. There was no reported perimeter intrusion. Instead, the application itself failed to consistently enforce access controls.
In cybersecurity terms, this resembles a broken authorization flaw. These issues are particularly dangerous because activity can appear legitimate within application logs, making detection harder than typical brute-force or malware-based attacks.
What Data Was Exposed?
Based on breach notices and media reporting, the PayPal SSN exposure may have included:
- Full names
- Email addresses
- Phone numbers
- Business addresses
- Social Security numbers
- Dates of birth
This combination is more than enough to facilitate identity theft or synthetic identity fraud. When SSNs and dates of birth are exposed together, criminals can open credit accounts, apply for loans, or create hybrid identities that blend real and fabricated data.
Unlike passwords, Social Security numbers cannot be changed. Once exposed, they may circulate in criminal ecosystems for years.
How a Business Logic Vulnerability Slipped Through
This PayPal Working Capital loan app bug highlights a persistent challenge in fintech security: business logic vulnerabilities.
Organizations such as NIST and CISA have long emphasized the importance of strict access control validation, especially in systems that process highly sensitive personal information.
Traditional security defenses are strong against malware and network-based attacks. They are less effective when the weakness lives inside the application’s authorization flow.
A single regression in access-control checks particularly in modules handling SSNs can quietly expose data without triggering classic intrusion detection alerts.
The six-month exposure window suggests the flaw was subtle. That’s often the nature of broken authorization issues: no alarms, no obvious breach signals, just unintended data visibility.
Who Is Most Affected?
The PayPal Working Capital breach primarily affected merchants and small businesses.
Unlike standard consumer PayPal accounts, Working Capital loans typically require additional personal identifiers. Many small-business owners use their SSN when applying for financing.
That means both personal and business identities may be at risk.
Beyond unauthorized transactions, potential risks include:
- Fraudulent loan applications
- Business credit manipulation
- Tax-related identity abuse
- Targeted phishing campaigns using accurate personal data
Even a relatively small exposure can create long-tail risk. Identity data retains value long after the original incident fades from headlines.
What PayPal Has Done So Far
According to public reporting, PayPal has taken the following steps:
- Rolled back the faulty code within 24 hours of discovery
- Reset passwords for affected accounts
- Refunded unauthorized transactions
- Issued breach notification letters in February 2026
- Offered two years of complimentary credit monitoring through Equifax
The company also reminded customers that it will never request passwords or one-time authentication codes via phone, SMS, or email a precautionary message aimed at reducing phishing attempts that often follow publicized breaches.
What You Should Do Now
Even if you did not receive a notification, this PayPal data breach is a practical reminder to review account security.
Strengthen Your Accounts
- Change your PayPal password to a unique, long passphrase.
- Enable multi-factor authentication (MFA) immediately.
- Update your primary email password if it is reused elsewhere.
Monitor Financial Activity
- Review PayPal transaction history carefully.
- Check linked bank and credit card statements for unfamiliar charges.
- Report suspicious activity promptly through official PayPal channels.
Protect Your Identity
- Enroll in the offered credit monitoring service if eligible.
- Place a fraud alert with major credit bureaus.
- Consider a credit freeze for stronger long-term protection if your SSN was exposed.
Stay Alert for Social Engineering
Expect phishing attempts referencing:
- Loan verification requests
- Account review notices
- Suspicious PayPal activity alerts
Always navigate directly to the official PayPal website or mobile app. Avoid clicking links in unsolicited emails or messages.
Broader Security Lessons
This incident reinforces several important cybersecurity principles:
- Business logic vulnerabilities can be as damaging as external hacks.
- Secure software development lifecycle (SDLC) processes must include access-control regression testing.
- Systems handling SSNs require strict segmentation and anomaly detection.
For IT teams, this underscores the need to validate authorization flows continuously not just at deployment.
For small businesses, it is a reminder that third-party financial platforms are extensions of your own risk surface.
FAQ: Understanding the PayPal Data Breach
Was the PayPal data breach caused by hackers?
PayPal states the issue was caused by a software bug in the Working Capital application, not a traditional external system compromise.
What is the PayPal Working Capital breach?
It refers to the exposure of sensitive customer data due to a PayPal Working Capital loan app bug that created an authorization flaw between July and December 2025.
What risks come from PayPal SSN exposure?
Major risks include identity theft, synthetic identity fraud, and targeted phishing or financial scams.
Should small businesses freeze credit after this PayPal data breach?
If Social Security numbers and dates of birth were exposed, placing a fraud alert or credit freeze is a prudent defensive step.
Final Thoughts
The confirmed PayPal data breach linked to its Working Capital loan system may have affected a limited number of users, but the sensitivity of the exposed data makes it significant.
When Social Security numbers are involved, risk doesn’t end with a password reset. Identity data can circulate long after the technical flaw is corrected.
For users, the response should be proactive: secure accounts, monitor financial activity, and remain vigilant against phishing attempts.
For the broader fintech ecosystem, this incident serves as a reminder that business logic and authorization controls deserve the same scrutiny as perimeter defenses. Sometimes the most consequential vulnerabilities are not loud they’re logical.
Calls to Action
- Review your PayPal security settings today.
- Enable MFA across all financial platforms.
- Share this article with other small-business owners using PayPal Working Capital.

