A widespread FortiGate firewall hacked campaign is actively unfolding, as threat actors carry out automated attacks designed to steal sensitive configuration data from exposed devices. Since January 15, 2026, security teams have observed attackers gaining unauthorized administrative access, exporting firewall configurations, and quietly creating new accounts to retain long-term control.
This FortiGate firewall attack in 2026 is especially concerning because it closely mirrors activity first seen in December 2025, shortly after Fortinet disclosed critical authentication bypass vulnerabilities related to FortiCloud single sign-on (SSO). Researchers warn that even organizations that patched promptly may still be exposed if attackers established persistence before remediation.
Incident Details and Timeline
Threat intelligence from Arctic Wolf shows that the latest wave of activity began in mid-January and follows a highly consistent, automated pattern. In many cases, attackers completed multiple stages of compromise in seconds, leaving little opportunity for defenders to intervene.
This Fortinet FortiGate security breach activity closely follows Fortinet’s December 2025 disclosure of two critical vulnerabilities:
- CVE-2025-59718 – Unauthenticated SAML SSO bypass
- CVE-2025-59719 – Unauthenticated SAML SSO bypass
These flaws affect systems running FortiOS, FortiWeb, FortiProxy, and FortiSwitchManager when FortiCloud SSO authentication is enabled.
In a recent update, Fortinet confirmed active exploitation of a FortiCloud SSO authentication bypass vulnerability, though it has not yet stated whether the January incidents rely on the same CVEs or on a modified or patched attack technique.
Who Is Affected in FortiGate Firewall Hacked
While Fortinet has not published official victim numbers, Arctic Wolf telemetry suggests that the FortiGate automated cyber attacks are impacting organizations across multiple regions, including North America, Europe, and Asia-Pacific.
- Enterprises operating internet-facing FortiGate firewalls
- Managed service providers (MSPs)
- Financial and professional services firms
- Technology companies with remote management enabled
Any organization with insufficiently restricted administrative access is at increased risk of FortiGate admin account compromise.
What Data and Systems Were Compromised
The attackers’ primary goal appears to be FortiGate configuration data theft. Stolen configuration files can contain:
- Firewall rules and access policies
- VPN configurations and credentials
- Administrative and hashed passwords
- Certificates, API keys, and internal network details
Security experts caution that once attackers obtain this information, they gain a detailed blueprint of an organization’s internal environment. This significantly increases the risk of follow-on attacks, even if the original vulnerability is later patched.
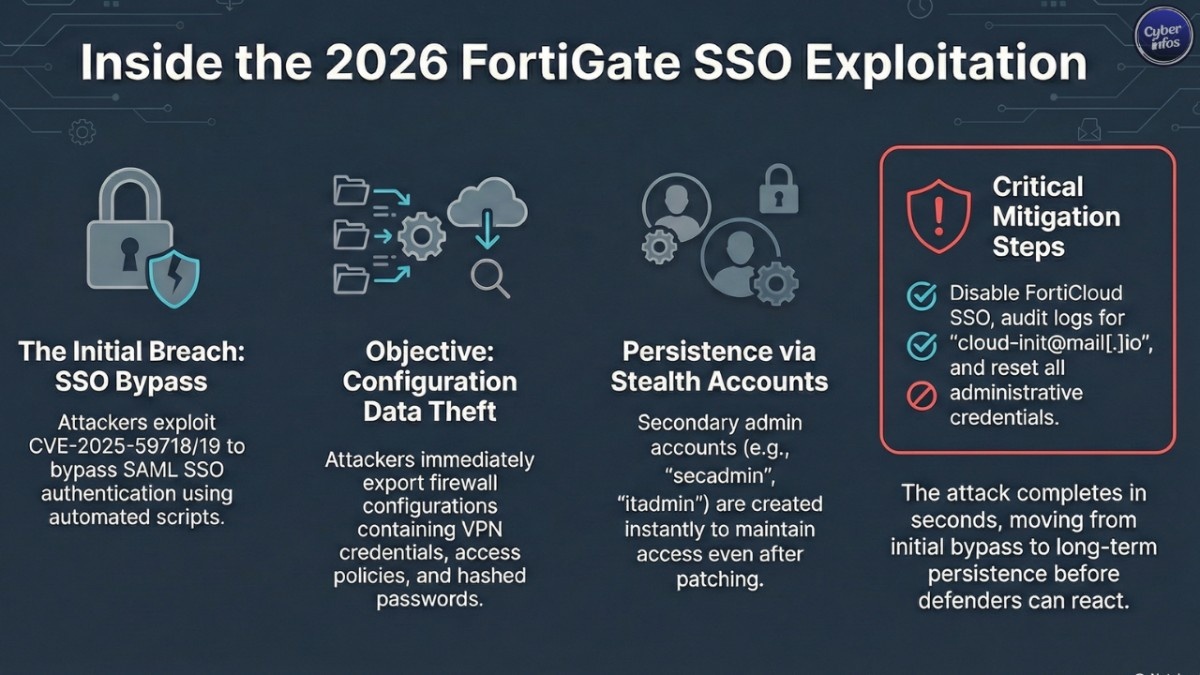
Technical Details of the Attack
Initial Access: FortiGate SSO Login Bypass Attack
According to Arctic Wolf, attackers initiate FortiGate SSO login bypass attacks from a small set of hosting provider IP addresses. One of the most frequently observed login accounts is:
cloud-init@mail[.]io
This access pattern strongly resembles earlier exploitation tied to CVE-2025-59718 and CVE-2025-59719, although investigators have not yet confirmed whether the same flaws are being reused.
Exfiltration: Configuration Data Theft
Immediately after successful authentication, attackers trigger a FortiGate configuration export using the device’s graphical management interface. The configuration file is then downloaded to the same external IP address used for the login, minimizing noise and avoiding additional infrastructure.
Persistence: Administrative Account Creation
To ensure continued access, attackers create multiple secondary administrator accounts. Commonly observed usernames include:
- secadmin
- itadmin
- support
- backup
- remoteadmin
- audit
Log analysis shows almost no delay between login, configuration export, and account creation, confirming the use of automated FortiGate exploitation scripts.
Indicators of Compromise (IOCs)
Organizations should urgently review FortiGate logs for the following FortiGate firewall IOC indicators:
Malicious Accounts
- cloud-init@mail[.]io
- cloud-noc@mail[.]io
Source IP Addresses
- 104.28.244[.]115
- 104.28.212[.]114
- 217.119.139[.]50
- 37.1.209[.]19
Unauthorized Admin Accounts
- secadmin, itadmin, support, backup, remoteadmin, audit
Current Status and Response
Arctic Wolf has enabled detections related to this Fortinet firewall vulnerability exploitation and is actively alerting customers when suspicious FortiGate activity is detected. Fortinet has acknowledged real-world exploitation and continues to issue updates through its PSIRT advisories.
However, the company has not yet confirmed whether existing patches fully mitigate this specific wave of attacks, making defensive hardening and threat hunting essential.
What Fortinet Users Should Do
- Apply all updates listed in Fortinet PSIRT security advisories.
- Hunt for known IOCs and review administrative activity logs.
- Reset all credentials if compromise is suspected, as exported password hashes can be cracked offline.
- Restrict FortiGate management access to trusted internal networks only.
- As a temporary mitigation, disable FortiCloud SSO if it is not required:
config system global
set admin-forticloud-sso-login disable
endExpert Analysis and Implications
Security analysts note that this Fortinet FortiGate security breach highlights a growing shift toward identity-based attacks against perimeter infrastructure. Rather than deploying ransomware, attackers are quietly harvesting configuration data and maintaining access, increasing the likelihood of future, more damaging intrusions.
The high level of automation suggests that mass exploitation will continue as long as exposed FortiGate devices remain reachable from the internet.
Company and Official Statements
Fortinet stated that it is “actively investigating reports of exploitation involving FortiCloud SSO” and reiterated that customers should apply all available patches and follow hardening best practices.
Arctic Wolf warned that organizations should assume compromise if unexplained FortiGate administrative logins or configuration exports are discovered.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. Is this a ransomware attack?
No. There is no evidence of ransomware. The attackers are focused on access and configuration data.
2. Can patched systems still be affected?
Yes. Devices may remain compromised if attackers created persistence accounts before patching.
3. Are other Fortinet products at risk?
Products affected by the same SSO vulnerabilities, including FortiWeb and FortiProxy, may also be impacted.
Final Thoughts
The ongoing FortiGate firewall hacked campaign underscores the importance of continuous monitoring, strict access controls, and proactive threat hunting. Cyber Infos will continue tracking this FortiGate firewall attack in 2026 and publish verified updates as more information becomes available.
Organizations should act decisively now—before stolen firewall configuration data is leveraged for deeper and more damaging attacks.

