Look, let’s reset expectations right away. Every January, security teams hear the same message: this year will be different. Better tools. Smarter automation. Fewer incidents. And yet, by March, inboxes are full of incident reports and late-night Slack pings again.
That’s why emerging malware 2026 isn’t just another annual prediction exercise. It’s a reality check.
Throughout 2025, I spent time reviewing breach write-ups, internal SOC timelines, and real-world response notes from environments running Microsoft 365, Google Workspace, AWS, and Azure. Nothing exotic. No fringe setups. And the pattern kept repeating. Malware didn’t win because it was advanced. It won because it was predictable and defenders were overloaded.
Attackers leaned into credential theft, OAuth token abuse, and trusted software paths. According to Verizon’s 2025 DBIR, 74% of breaches involved credential misuse. No zero-days. No Hollywood hacking scenes. Just access.
Now heading into 2026, new malware families are building directly on those lessons. They’re quieter. They’re more selective. And they increasingly rely on AI-powered malware techniques to reduce mistakes and maximize payoff.
Why should you care? Because defenses built for loud malware don’t catch patient threats. And patience is where attackers are winning right now.
Malware Evolution in 2025: Setting the Stage for 2026
Here’s the thing. 2025 wasn’t about innovation. It was about optimization.
Infostealers quietly harvested credentials from browsers and endpoint caches. Loaders evolved into modular delivery platforms that could swap payloads without reinfection. Ransomware groups realized encryption wasn’t always necessary—data theft alone created enough leverage.
I reviewed one October 2025 incident where attackers maintained VPN access for 94 days using valid credentials. Ninety-four days. No malware alerts. No suspicious binaries. Just normal-looking logins at inconvenient hours.
That model carries straight into 2026.
Malware trends shifted away from brute force toward persistence and blending in. Threat actors figured out something defenders already knew: SOC teams are drowning in alerts. So attackers reduced noise. Fewer crashes. Fewer obvious indicators. More waiting.
And when malware waits, detection gets much harder.

AI-Powered Malware
Machine Learning in Attack Chains
AI-powered malware isn’t about superintelligence. It’s about automation making better decisions than static scripts ever could.
Instead of hard-coded logic, malware now evaluates context. Is the system valuable? Is the user active? Is this endpoint protected by Microsoft Defender, CrowdStrike, or SentinelOne? Did security tooling interfere last time?
Based on those answers, the malware decides whether to execute, delay, or quietly exit. I’ve seen late-2025 samples that paused execution for weeks after a failed attempt. Weeks. Why rush when patience avoids detection?
Automated Target Selection
Here’s where attackers get efficient.
Malware enumerates user roles, installed applications, and cloud permissions. Finance users. Admin accounts. DevOps engineers. High-value targets trigger advanced payloads. Everyone else becomes lateral movement infrastructure.
Think of this, A junior developer’s laptop gets infected. Nothing happens. Two weeks later, the same network sees a finance login. Different payload. Same malware family.
That’s not a thought experiment. That’s happening.
Adaptive Evasion Techniques
Traditional malware either runs or crashes. AI-driven malware adapts.
If an endpoint agent blocks execution, the malware sleeps. If memory hooks are detected, execution paths change. Some variants uninstall themselves entirely to avoid forensic capture, then reappear days later through scheduled tasks or cloud persistence mechanisms.
Frustrating? Absolutely. Effective? Unfortunately, yes.
ChatGPT-Generated Malicious Code
Tools inspired by FraudGPT and WormGPT didn’t make attackers brilliant. They made them fast.
Attackers now generate phishing kits, PowerShell loaders, and obfuscated JavaScript in minutes. The code isn’t perfect. It doesn’t need to be. At scale, “good enough” wins.
Bottom line: AI-powered malware reduces attacker effort and increases defender fatigue. That’s the real shift.
Polymorphic & Metamorphic Threats
How They Evade Detection
Every execution looks different. Different hashes. Different instruction order. Same behavior.
Signature-based tools fall apart here. SOC teams end up chasing what looks like endless “new” samples that are actually the same threat wearing different disguises.
New Obfuscation Techniques
Modern variants delay decryption until very specific conditions are met—business hours, trusted IP ranges, real mouse movement. Sandboxes never see the real payload.
Here’s the catch. If your detection strategy relies heavily on detonation, you miss everything that matters.
Case Study: Recent Variant
In November 2025, a polymorphic loader targeting SaaS admins lived entirely in memory for 61 days inside a retail environment. No dropped files. No obvious persistence.
The only clue? Unusual PowerShell parent-child relationships. That’s it.
Detection Strategies
Behavioral analysis wins. Memory inspection wins. Correlation over time wins.
Static signatures don’t.
Supply Chain Malware
Real talk—this is one of the most damaging malware trends heading into 2026.
Software Update Hijacking
Attackers stopped breaking into applications. They broke into update mechanisms.
A poisoned update looks legitimate. Signed. Trusted. Automatically deployed. By the time someone notices, it’s already everywhere.
Compromised Dependencies
Third-party libraries remain a goldmine. In August 2025, Sonatype reported over 11,000 malicious open-source packages discovered in a single month. That’s not edge-case risk. That’s daily developer reality.
NPM/PyPI Package Threats
Typosquatting still works because humans make mistakes. A single mistyped package name can introduce backdoors that sit dormant for months.
Hardware-Level Backdoors
Still rare. Still terrifying.
Firmware-level implants survive OS rebuilds. If you’ve ever had to explain that remediation requires hardware replacement, you know how painful that conversation gets.
Notable Incidents from Late 2025
Several large enterprises learned that “we trust our vendors” isn’t a control. Inventory, verification, and monitoring matter. A lot.
Mobile Malware Evolution
Android Malware Trends
Android malware increasingly abuses accessibility services, sideloaded enterprise apps, and fake update mechanisms. I’ve personally seen banking trojans hidden inside QR scanners and flashlight apps. Yes, really.
iOS Emerging Threats
iOS attacks focus less on mass infection and more on surveillance. Configuration profile abuse and enterprise certificate misuse enable quiet monitoring without classic malware indicators.
Banking Trojans 2.0
Modern banking malware targets live sessions. MFA codes. Real-time transfers. Blink and the money’s gone.
Spyware as a Service
Commercial spyware lowered the barrier to entry. Surveillance capabilities once limited to nation-states are now rentable by private actors.
Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS) Updates
New Affiliate Models
Affiliates now get dashboards, performance metrics, and revenue splits. It looks disturbingly like a legitimate SaaS business.
Double and Triple Extortion
Encryption is optional now. Data theft, regulatory pressure, and customer notification threats carry more leverage.
Data Leak Site Innovations
Leak sites added previews, search features, and timed disclosures. Psychological pressure is part of the attack strategy.
Payment Tracking Challenges
Cryptocurrency laundering evolves faster than regulation. That’s a constraint defenders have to accept.
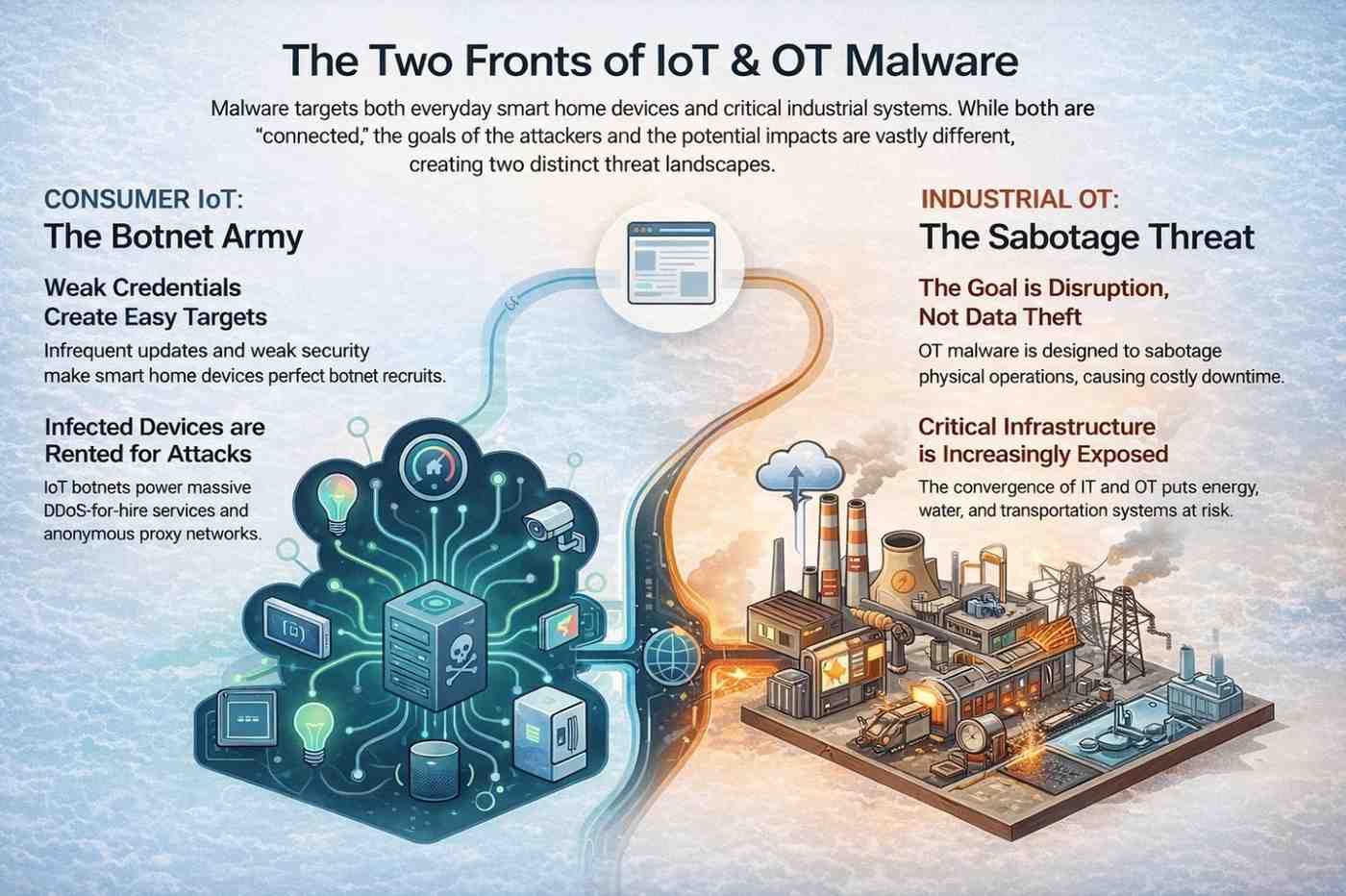
IoT and OT Malware
Smart Home Device Targeting
Weak credentials and rare updates make consumer IoT devices perfect botnet recruits.
Industrial Control System Threats
OT malware doesn’t steal data. It disrupts operations. Downtime alone can cost millions.
Botnet Expansion
IoT botnets power DDoS-for-hire services and anonymous proxy networks at massive scale.
Critical Infrastructure Risks
Energy, water, and transportation systems face growing exposure as IT and OT environments converge.
Indicators of Compromise (IOCs)
File Hashes to Watch
Useful, but short-lived. Treat them as signals, not solutions.
Suspicious Network Patterns
Beaconing traffic. Odd DNS behavior. Unusual TLS fingerprints.
Registry Key Modifications
Persistence hides in boring places. Look there.
Behavioral Indicators
Unexpected process relationships and abnormal resource use matter more than any hash.
Protection Strategies
EDR/XDR Implementation
Tune it. Staff it. Focus on behavior, not alert volume.
Network Segmentation
Containment limits blast radius. Every time.
Application Whitelisting
Annoying? Yes. Effective? Also yes.
Security Awareness Training
Humans still matter. Train for realistic scenarios.
Threat Intelligence Feeds
Context saves time. Time saves money.
Final thoughts
Here’s the takeaway.
Emerging malware 2026 isn’t about flashy exploits. It’s about patience, context, and scale. The new malware families you’ll face this year won’t announce themselves. They’ll blend in, wait, and monetize quietly.
I’ve seen teams succeed by focusing on visibility, behavioral detection, and response speed. Fancy tools help. Discipline helps more.
Stay curious. Stay skeptical. And don’t assume last year’s defenses will save you this year.
Because they won’t.

