Imagine downloading a seemingly harmless QR scanner or a handy expense tracker from the Google Play Store, only to find out it’s a wolf in sheep’s clothing. This isn’t a hypothetical scenario—it’s a reality that has affected millions of Android users.
Recently, security researchers at Bitdefender uncovered a massive ad fraud campaign involving 331 malicious apps that collectively racked up over a 60 million downloads. These apps didn’t just annoy users with intrusive ads; they exploited vulnerabilities in Android 13 to bypass security restrictions, steal credentials, and carry out phishing attacks.
Let’s dive into how this happened, what it means for users, and how we can protect ourselves in an increasingly risky digital landscape.
How These Apps Fooled Everyone
At first glance, these apps appeared to be legitimate tools. They masqueraded as:
- QR code scanners
- Expense trackers
- Health and fitness apps
- Wallpaper customization tools
These are the kinds of apps we download without a second thought. After all, who doesn’t need a quick way to scan a QR code or track their daily expenses? But beneath their innocent exteriors, these apps were anything but benign.
Once installed, they unleashed a barrage of intrusive full-screen ads, even when the app wasn’t actively in use. Some went a step further, attempting to phish sensitive information like online service credentials and credit card details.
What’s truly alarming is that these apps achieved all this without requiring the permissions typically associated with such actions. This level of sophistication suggests a deep understanding of Android’s inner workings and a willingness to exploit it.
How They Evaded Detection: A Masterclass in Deception
The developers behind these malicious apps employed a variety of techniques to fly under the radar. Here’s how they did it:
Icon Hiding: Out of Sight, Out of Mind
These apps used clever tricks to hide their icons from the launcher, making them invisible to users. One method involved leveraging APIs designed for Android TV (LEANBACK_LAUNCHER), which aren’t typically monitored as closely.
Activity Launching: Sneaky Phishing Attacks
By abusing APIs like `DisplayManager.createVirtualDisplay` and `Presentation.show()`, the apps could launch activities without user interaction. This allowed them to display full-screen phishing prompts mimicking legitimate services like Facebook or YouTube.
Persistence Mechanisms: Staying Put
The apps used dummy broadcast receivers and foreground services to maintain their presence on devices. Even on newer Android versions, where foreground services are restricted, the attackers circumvented these limitations using native code.
Advanced Obfuscation: Staying Under the Radar
To avoid detection by security systems and researchers, the malware employed:
- String obfuscation using XOR encoding.
- Polymorphic encryption techniques combining AES and Base64.
- Runtime checks to detect emulated environments or debugging attempts.
- Native libraries obfuscated with tools like Armariris.
When and How This Unfolded
Most of these malicious apps became active on Google Play during Q3 of 2024. Initially, they appeared as benign applications, but updates in early Q3 introduced the malware components.
The campaign is still active, with the latest batch of malware uploaded to the Play Store as recently as March 4, 2025. At the time of Bitdefender’s investigation, 15 of these apps were still available for download.
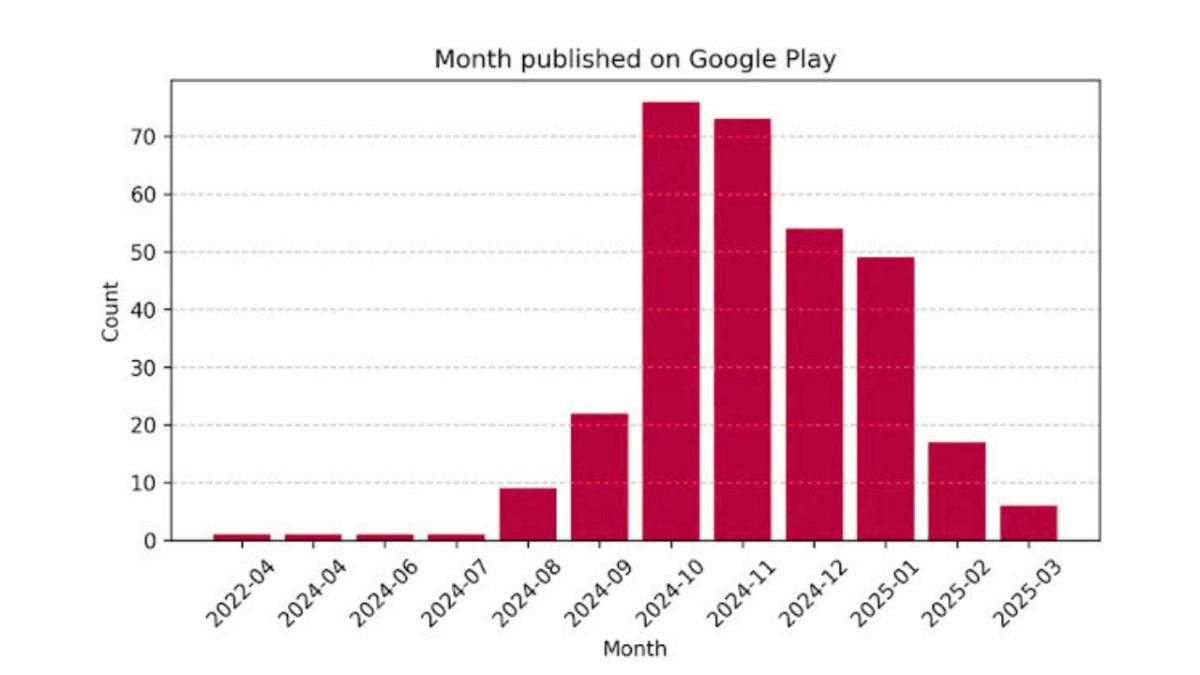
Scale of the Problem: A Global Threat
While the exact geographical distribution of affected users is unclear, the sheer number of downloads—over 60 million—suggests a widespread impact across multiple regions.
This campaign is unprecedented in scale and sophistication, indicating that the attackers are either a single, highly organized entity or a group using the same packaging tools purchased from black markets.
What This Means for Users: A Wake-Up Call
This discovery is a stark reminder that even trusted platforms like the Google Play Store aren’t immune to malicious actors. While Google has taken steps to remove these apps, the attackers continue to adapt their methods, making it a game of cat and mouse.
Key Takeaways for Users:
- Don’t Rely Solely on Default Protections: Android and the Google Play Store offer some level of security, but they’re not foolproof. Consider using a reputable third-party security solution for added protection.
- Be Cautious with App Permissions: If an app asks for permissions that seem unnecessary for its functionality, think twice before granting them.
- Read Reviews and Do Your own Research: Before downloading an app, check its reviews and ratings. Be wary of apps with few downloads or overly generic descriptions.
- Keep Your Device Updated: Ensure your Android device is running the latest version of the operating system, as updates often include security patches.
Personal Reflection
As someone who relies heavily on my smartphone for both work and personal use, this news hits close to home. I’ve downloaded my fair share of utility apps, trusting that the Google Play Store would keep me safe.
But this incident serves as a reminder that trust isn’t enough. In today’s digital age, we need to be proactive about our security. It’s not just about protecting our devices; it’s about safeguarding our personal information, our finances, and our privacy.
Final thoughts
This campaign isn’t just a wake-up call for users—it’s a call to action for developers and platform providers. As attackers grow more sophisticated, the need for robust security measures becomes increasingly urgent.
Google has made strides in improving Android’s security, but this incident shows that there’s still work to be done.
For users, the lesson is clear: stay vigilant. Even in trusted spaces, threats can lurk in the shadows. By staying informed and taking proactive steps to protect ourselves, we can navigate the digital world with greater confidence and security.
In the end, the battle against malicious apps is ongoing. But with awareness, caution, and the right tools, we can stay one step ahead of the attackers. Let’s not wait for the next big breach to take action—start securing your digital life today.

