Browser extensions have become a normal part of everyday internet use. Most users install them quickly, assuming that anything listed in an official store has already been checked and approved. Unfortunately, that sense of safety is now being exploited.
A recently identified cybercrime operation known as Stanley demonstrates how malicious Chrome extensions are being used to carry out highly effective phishing campaigns directly inside the browser. Rather than relying on suspicious emails or fake links, attackers embed phishing functionality into extensions and distribute them through trusted platforms, driving a sharp increase in Chrome Web Store phishing.
This shift represents a major evolution in browser extension malware, where user trust has become more valuable to attackers than technical sophistication.
A New Malware-as-a-Service Model
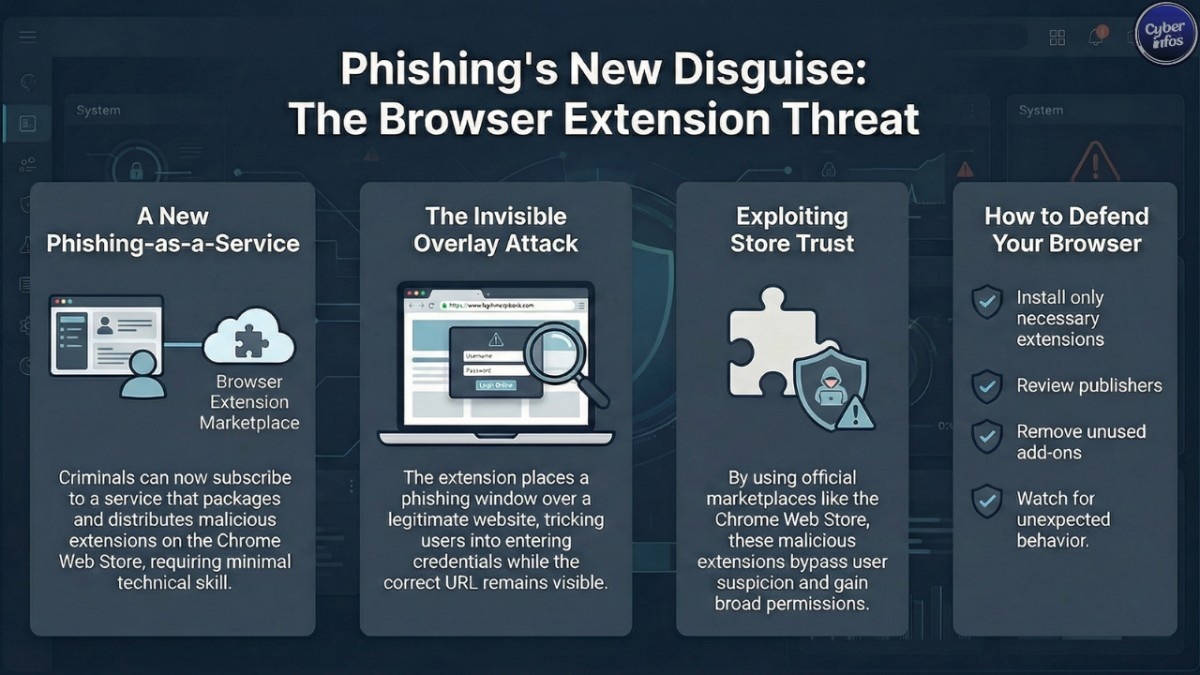
Security researchers identified Stanley as a subscription-based malware-as-a-service offering promoted within cybercrime communities. What sets it apart is its promise to handle distribution, including publishing phishing-enabled extensions on the Chrome Web Store.
By removing the complexity of delivery, Stanley enables MaaS cybercrime operations that can be launched by attackers with minimal technical skill. Access is simple: pay for the service, deploy the extension, and begin phishing.
How the Attack Works
The core technique behind Stanley involves iframe phishing attacks, which rely on visual deception rather than exploiting browser vulnerabilities.
After installation, the extension operates quietly in the background:
- It monitors user navigation activity
- At selected moments, it overlays the page with a full-screen iframe
- The iframe displays attacker-controlled phishing content
- The legitimate website address remains visible in the browser bar
Because everything appears normal, victims rarely question what they see. This makes the technique a particularly effective form of browser-based phishing.
Why Browser Extensions Are a High-Value Target
Browser extensions operate with persistent access and broad permissions, making them especially attractive for phishing via browser extensions.
For attackers, extensions provide:
- Continuous background operation
- Direct interaction with trusted websites
- Long-term access without repeated user interaction
- Limited visibility to many traditional security tools
As a result, Google Chrome extension threats are no longer edge cases—they are becoming a mainstream attack vector.
Command-and-Control and Persistence
Stanley-based extensions maintain persistent communication with attacker infrastructure. They regularly poll command-and-control servers, allowing operators to adjust behavior in real time.
This enables attackers to:
- Enable or disable phishing activity instantly
- Send deceptive browser notifications
- Modify targeting based on location or user behavior
- Rotate infrastructure to avoid takedowns
The result is a durable and adaptive phishing attack infrastructure.
Monetization Through Subscription Tiers
Stanley is sold through multiple subscription levels. Higher-tier plans include centralized management panels, customization features, and guidance on publishing malicious extensions.
By commercializing Chrome extension security evasion, Stanley transforms phishing into a repeatable business model, which is a defining characteristic of modern malware-as-a-service operations.
Abuse of Trusted Marketplaces
The most concerning aspect of this campaign is its reliance on trusted distribution platforms. Extensions published through the Google Chrome Web Store automatically benefit from user confidence.
Past investigations have shown that browser extension malware can remain available for extended periods, quietly collecting data and credentials before being detected and removed.
Technical Simplicity, Strategic Impact
Despite its effectiveness, Stanley’s codebase is not particularly advanced. Researchers describe it as inconsistent and loosely structured.
Its success comes from strategy rather than sophistication. By prioritizing distribution, persistence, and trust, Stanley enables large-scale browser-based phishing without advanced exploits.
Defensive Guidance for Users and Organizations
Reducing exposure to malicious Chrome extensions starts with basic hygiene:
- Install only necessary extensions
- Review publishers and update history
- Remove unused or outdated add-ons
- Watch for unexpected overlays or notifications
Organizations should complement these steps with allowlisting, browser isolation, and monitoring focused on Chrome extension security.
Why This Threat Matters
Stanley reflects a broader change in attacker behavior. Phishing is no longer limited to emails or cloned websites it is now embedded directly within everyday tools.
As phishing via browser extensions continues to grow, ignoring extension risk is no longer viable. This evolving phishing attack infrastructure is designed for stealth, scale, and persistence.
Final Thoughts
The growing threat of malicious Chrome extensions shows how attackers are shifting away from noisy tactics and toward stealthy abuse of trust. By using official platforms, Chrome Web Store phishing allows browser extension malware to blend into everyday browsing without raising suspicion. Victims may see legitimate websites and correct URLs, while browser-based phishing quietly operates in the background.
This rise in phishing via browser extensions signals a major change in attacker strategy. As Google Chrome extension threats become more common, treating extensions as low-risk tools is no longer viable. Stronger awareness and tighter controls around Chrome extension security are now essential. In modern attacks, the most dangerous threats don’t look suspicious they look completely normal.

