The Claude artifacts ClickFix macOS infostealer campaign marks a troubling evolution in search-based malware attacks. Threat actors are now abusing public AI-generated content to trick macOS users into infecting themselves simply by copying and pasting commands into Terminal.
Researchers from MacPaw’s Moonlock Lab and AdGuard have uncovered multiple malicious campaigns that leverage public artifacts hosted on Anthropic’s Claude platform. These fake guides appear in Google Search results for common macOS queries such as “Homebrew install,” “online DNS resolver,” and “macOS disk space analyzer.”
At least 15,000 users reportedly viewed one of these malicious guides before it was flagged. The true number of victims remains unclear, but the technique is concerning because it exploits trust in AI-generated documentation and search results two resources people increasingly rely on daily.
This is not just another phishing attempt. It’s a carefully staged social engineering attack that blends AI content, Google Ads promotion, and command-line deception to deploy the MacSync infostealer on macOS devices.
Incident Overview: AI Content Weaponized for Malware Delivery
The attack begins in Google Search. Cybercriminals purchase ads or manipulate search rankings so their malicious links appear at the top for popular macOS-related queries.
Victims who click these results are redirected to one of two places:
- A public Claude artifact page hosted on the claude.ai domain
- A fake Apple Support-style article hosted on Medium
In both scenarios, the content looks professional and technical. It walks users through what appears to be legitimate troubleshooting or installation instructions. The final step? Paste a provided command into Terminal.
According to Moonlock Lab researchers, one Claude artifact alone accumulated more than 15,600 views. AdGuard researchers previously recorded over 12,000 views days earlier suggesting rapid spread.
Both variants ultimately lead to the same malicious infrastructure, indicating a coordinated operation.
This campaign closely mirrors earlier ClickFix attacks abusing shared conversations on OpenAI’s ChatGPT and xAI’s Grok platform, signaling a broader trend: large language model platforms are becoming delivery vehicles for malware.
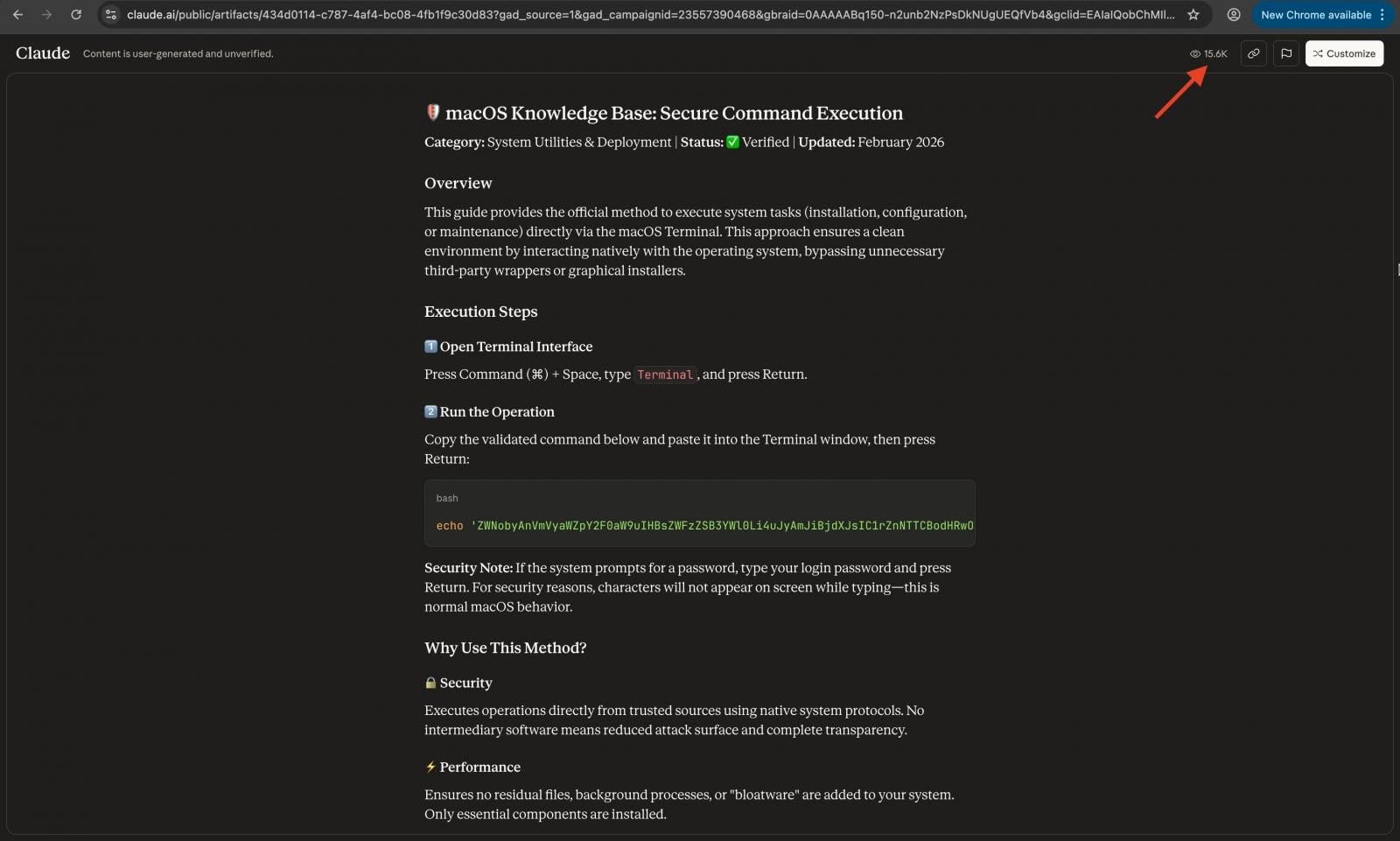
How the Claude Artifacts ClickFix macOS Infostealer Works
At a high level, this attack tricks users into running a malicious shell command disguised as a helpful fix.
Two command variants have been observed:
- A base64-encoded command piped into zsh
- A curl command downloading a remote payload and executing it
In plain language, here’s what’s happening:
- The command downloads hidden code from a remote server.
- That code installs a malware loader.
- The loader deploys the MacSync infostealer.
Think of it like being handed a sealed package and told it contains helpful instructions — but once opened, it quietly installs spyware.
Technical Breakdown (For IT Professionals)
Once executed, the script:
- Connects to command-and-control (C2) infrastructure using a hardcoded token and API key.
- Spoofs a macOS browser user-agent to blend in with legitimate traffic.
- Pipes responses directly into
osascript, which runs AppleScript routines to extract sensitive data.
The malware targets:
- macOS Keychain credentials
- Browser-stored passwords
- Cryptocurrency wallet data
- Session tokens
Stolen data is compressed into /tmp/osalogging.zip and sent via HTTP POST to a remote C2 endpoint. If exfiltration fails, the archive is split into smaller chunks and retried up to eight times.
After successful exfiltration, the malware performs cleanup to erase traces.
The efficiency and automation suggest an experienced threat actor.
Who Is at Risk?
The Claude artifacts ClickFix macOS infostealer campaign primarily targets:
- macOS users searching for developer tools
- Homebrew users
- Cryptocurrency holders
- IT professionals testing CLI utilities
- Small businesses relying on macOS workstations
Users who frequently copy Terminal commands from blogs, forums, or AI tools are at the highest risk.
Small businesses may face operational disruption if compromised credentials allow attackers into SaaS dashboards, payment processors, or cloud infrastructure.
For IT teams, the threat highlights a new attack surface: trusted AI-generated content.Claude Artifacts ClickFix
How to Protect Yourself and Your Organization
- Never blindly paste Terminal commands
If you don’t fully understand what a command does, do not execute it. Break it down and inspect each part. - Decode base64 strings before running them
If a command includesbase64 -Dor similar, decode it first in a safe environment to review its contents. - Verify URLs carefully
Check for subtle domain variations. Attackers often use similar-looking domains to trick users. - Enable endpoint protection
Use reputable macOS security tools capable of detecting infostealers and suspicious script execution. - Monitor outbound network traffic
IT teams should monitor for unusual HTTP POST traffic to unknown domains. - Restrict administrative privileges
Limit who can execute privileged commands on organizational devices. - Enable multi-factor authentication (MFA)
Even if credentials are stolen, MFA can prevent account takeover. - Train staff on AI-assisted risks
Include AI-generated documentation in your security awareness training programs. - Use ad-blocking solutions
AdGuard researchers noted that malicious Google ads played a role. Blocking ads reduces exposure. - Ask the AI before running the command
Ironically, one of the safest steps is asking the same chatbot:
“Is this command safe? What exactly does it do?”
Expert Response and Industry Implications
Security researchers warn that AI platform abuse will likely increase.
LLM platforms allow public sharing of artifacts and conversations. While these tools include disclaimers stating content is user-generated and unverified, many users overlook these warnings.
This attack doesn’t exploit a vulnerability in Claude itself. Instead, it exploits human trust in AI-generated technical documentation.
The broader implication? Search engines, AI platforms, and users must adapt to a reality where helpful-looking AI content may conceal malware.
Additional Safety Tips
- Regularly audit your macOS Keychain for unused credentials.
- Use a password manager that alerts you to breaches.
- Review installed Launch Agents and cron jobs for suspicious persistence mechanisms.
For broader protection strategies, review our guide to phishing prevention and read more about ransomware trends affecting macOS environments.
FAQ: Claude Artifacts ClickFix macOS Infostealer
What is the Claude artifacts ClickFix macOS infostealer?
It’s a malware campaign that uses public AI-generated Claude artifacts and Google Search ads to trick macOS users into running malicious Terminal commands that install the MacSync infostealer.
How can I tell if I’m infected?
Look for unusual outbound network traffic, unknown Launch Agents, unexpected password resets, or suspicious files in /tmp. Security software may also detect infostealer behavior.
Is Claude unsafe to use?
Claude itself is not compromised. The issue stems from malicious user-generated content shared publicly on the platform.
What should I do if I executed the command?
Immediately disconnect from the internet, run a full security scan, change all passwords from a clean device, enable MFA, and monitor financial accounts.
Are other AI platforms being abused this way?
Yes. Similar ClickFix campaigns have reportedly abused shared conversations on ChatGPT and Grok, indicating a broader trend.
Final Thoughts
The Claude artifacts ClickFix macOS infostealer campaign highlights a new era of cybercrime one where AI-generated content becomes a delivery vehicle for malware.
This attack doesn’t rely on exploits or zero-days. It relies on trust. Trust in search results. Trust in AI documentation. Trust in helpful-looking guides.The good news? The defense is awareness.
Pause before pasting. Inspect before executing. Verify before trusting. Cybersecurity isn’t just about firewalls and antivirus anymore it’s about critical thinking in the age of AI.
Stay ahead of emerging threats: Join our WhatsApp Channel for real-time security alerts.
Follow us on LinkedIn for daily cybersecurity insights and breaking news.

