The days of easy cyber insurance approvals are over. In 2026, insurers aren’t simply issuing policies—they’re demanding strong proof that your organization is a secure, low-risk applicant. With ransomware claims averaging over $631,000 and new compliance obligations tightening across industries, underwriters now operate more like auditors than traditional insurers.
If you want to secure the best cyber liability insurance cost and avoid being turned down, you need far more than a completed application form. What you really need is a well-documented, mature security posture.
This guide delivers a comprehensive, expert-backed step-by-step checklist to prepare your business for cyber insurance. You’ll see exactly what underwriters expect, which documents you must gather, and what actions can help reduce premiums while securing reliable data breach liability coverage.
Why Cyber Insurance Requirements Are Getting Stricter
Before reviewing the checklist, it’s important to understand why today’s approval process is far more demanding.
Between 2020 and 2023, carriers absorbed massive losses from the surge in ransomware and social engineering incidents. As a result, they significantly tightened their underwriting criteria. According to 2025 industry insights, premiums have leveled off—some markets even seeing a 6% decrease—but eligibility standards have risen considerably.
Carriers are no longer satisfied with “good enough” security. They now require “evidence-based” security. Without certain foundational controls—such as Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) or Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR)—you won’t just face higher pricing; you may be denied coverage altogether.
What Insurers Are Actually Looking For
- Risk Maturity: Do you fully understand your vulnerabilities?
- Resilience: If you’re attacked, can you recover without needing the insurer to cover everything?
- Compliance: Are you meeting requirements such as GDPR, HIPAA, or PCI-DSS?
The Ultimate Step-by-Step Checklist to Prepare Your Business for Cyber Insurance
Use this checklist to evaluate your security posture before requesting commercial cyber insurance quotes.
1. Implement Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) Everywhere
MFA has become the basic requirement—essentially the seatbelt of cyber insurance. Without it, your application is nearly certain to be declined.
- Requirement: Enable MFA for email, remote access (VPNs), and privileged administrative accounts.
- Pro Tip: SMS-based 2FA is often viewed as weak. Insurers prefer app-based authenticators like Google Authenticator or Microsoft Authenticator, or hardware devices such as YubiKeys.
2. Deploy Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR)
Traditional antivirus alone isn’t adequate anymore. Insurers expect EDR platforms capable of using AI to analyze behavior and stop attacks in real time.
- Why it matters: EDR demonstrates your ability to identify and contain intruders before they can encrypt or steal your data.
- Top Tools: CrowdStrike, SentinelOne, Microsoft Defender for Endpoint.
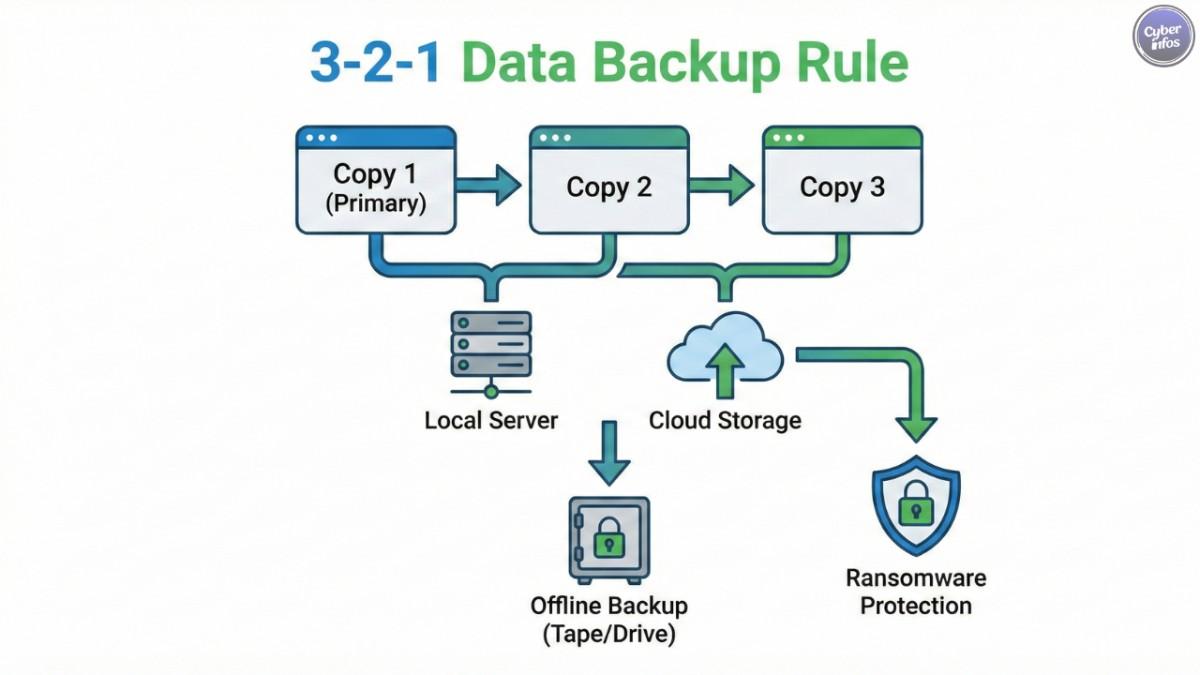
3. Fortify Your Backup and Disaster Recovery Strategy
If ransomware strikes, your backups become the key to recovery. Underwriters examine this closely because it directly affects business interruption coverage.
- The 3-2-1 Rule: Keep 3 copies of your data, stored on 2 different media types, with 1 copy offsite and offline (immutable).
- Testing: You must be able to prove that backups are tested regularly. A backup that has never been restored in testing creates significant risk.
4. Patch Management and Vulnerability Scanning
Unpatched systems remain one of the most common breach vectors.
- Checklist Item: Implement automated patch management and ensure critical updates are applied within 14–30 days of release.
- Action: Perform monthly vulnerability scans to identify weaknesses before attackers exploit them.
5. Employee Training and Phishing Simulations
Human error consistently contributes to more than 80% of breaches, making training a non-negotiable requirement for insurers.
- Requirement: Conduct mandatory cybersecurity awareness training annually at minimum—quarterly is even better.
- Proof: Maintain records of phishing simulations and click rates to demonstrate ongoing improvement.
6. Create and Test Your Incident Response Plan (IRP)
An unwritten or untested plan won’t meet insurer expectations. Your IRP must be documented, distributed, and practiced.
- What to include: Outline immediate points of contact—legal counsel, the insurance hotline, your PR team, and internal responders.
- Tabletop Exercises: Insurers highly value evidence of a tabletop exercise conducted within the past year.
Essential Documentation You Need to Have Ready
When applying, vague answers won’t help. You must provide proof of your security measures. Having these documents prepared can speed underwriting and potentially reduce your cyber insurance premiums.
| Document Category | Specific Requirements |
|---|---|
| Network Security | Network diagrams, firewall configuration logs, MFA implementation report. |
| Policies & Procedures | Written Information Security Program (WISP), Acceptable Use Policy, BYOD Policy. |
| Incident Response | A current Incident Response Plan (IRP), Disaster Recovery Plan (DRP), call trees. |
| Vendor Management | List of third-party vendors with data access, Service Level Agreements (SLAs). |
| Compliance | Documentation showing adherence to applicable laws such as HIPAA, CCPA, or GDPR. |
Warning: Misrepresentation is the number one cause of claim denials. If you mark “Yes” for MFA but only half your accounts use it, the insurer can legally reject a claim during an incident. Be completely accurate.
How to Lower Your Cyber Insurance Premiums
- Higher Deductibles: Selecting a higher retention signals confidence in your security posture and often leads to reduced premiums.
- Bundle Policies: Determine whether your current business owner’s policy (BOP) offers a cyber option, though standalone policies generally provide stronger ransomware coverage.
- Use an Expert Broker: Specialized cyber insurance brokers understand which carriers align best with your industry and risk profile.
- Certifications: Earning SOC 2 Type II or ISO 27001 certification can dramatically improve your standing with underwriters.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What does cyber liability insurance cover?
It generally covers expenses related to data breaches, including legal fees, notification costs, ransomware payments, business interruption coverage, and forensic investigations.
2. How much does cyber insurance cost for a small business?
In 2025, typical costs range from $1,500 to $5,000 annually, depending on industry, revenue, and security controls. High-risk sectors like healthcare or finance often pay more.
3. Can I get cyber insurance without MFA?
It’s extremely difficult. Most reputable carriers treat MFA as a mandatory control. If coverage is offered without it, the limits will likely be lower and premiums significantly higher.
4. What is the difference between first-party and third-party coverage?
First-party coverage addresses your direct losses—such as data recovery and lost income. Third-party coverage applies if clients or partners sue because their data was compromised through your systems.
5. Why was my cyber insurance application denied?
Common reasons include the absence of MFA, running unpatched or end-of-life software, weak backup practices, or failing to disclose previous cyber incidents.
6. Do I need cyber insurance if I use cloud services like AWS or Microsoft 365?
Yes. Cloud providers protect the infrastructure, but you are responsible for securing your data and access. If an employee’s account is compromised, Amazon or Microsoft isn’t liable—you are.
Final thoughts
Preparing for cyber insurance is no longer a simple administrative task—it’s an essential evaluation of your organization’s overall security health. By following this step-by-step checklist to prepare your business for cyber insurance, you’re not just meeting insurer expectations; you’re strengthening your business against evolving threats.
Cyber risk shifts constantly, so don’t wait for renewal season to begin improving your defenses. Implement these controls now to secure stronger coverage, reduce premiums, and achieve greater peace of mind.
Ready to take the first step? Start by reviewing your MFA deployment today—it remains the single most impactful control you can implement.